Developing fine motor skills Math Worksheets for Ages 3-8
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Developing Fine Motor Skills Math Worksheets for Ages 3-8" are designed to enhance your child’s math and motor proficiency simultaneously. Engaging activities like tracing, drawing, and cutting not only introduce fundamental math concepts but also strengthen hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and pencil grip. These printable worksheets blend fun with learning, featuring vibrant illustrations and hands-on exercises that make math enjoyable. Ideal for preschoolers through early elementary students, each worksheet encourages mastery of key skills while fostering a love for math. Discover the perfect resource for building confidence and honing essential abilities. Download now to start your child’s journey to skillful success!
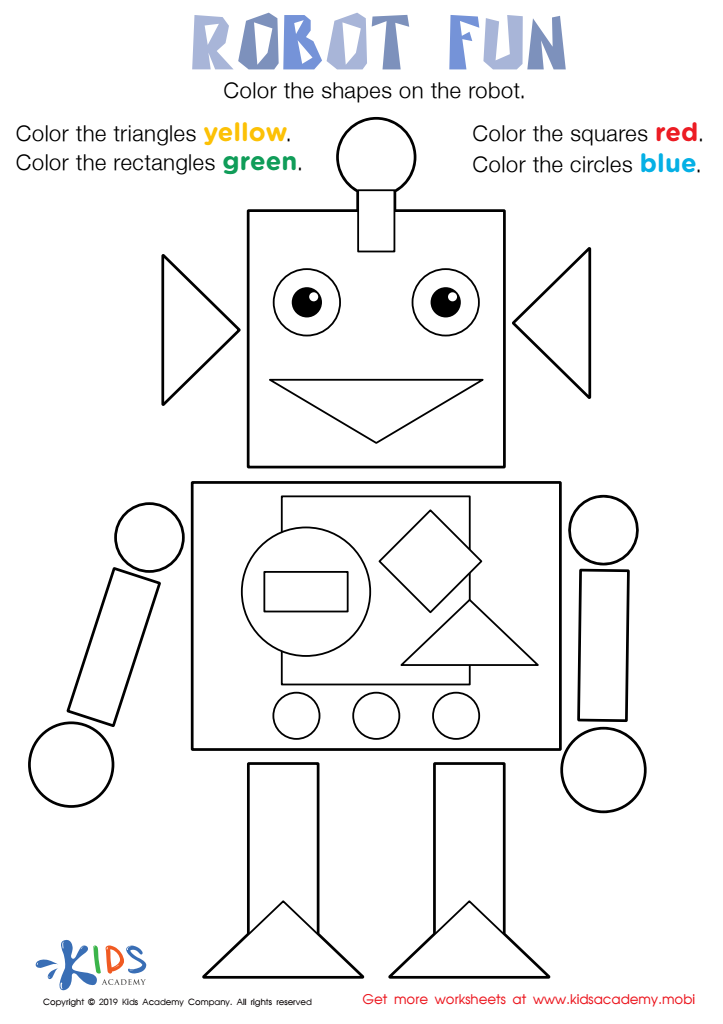

Robot Fun Worksheet
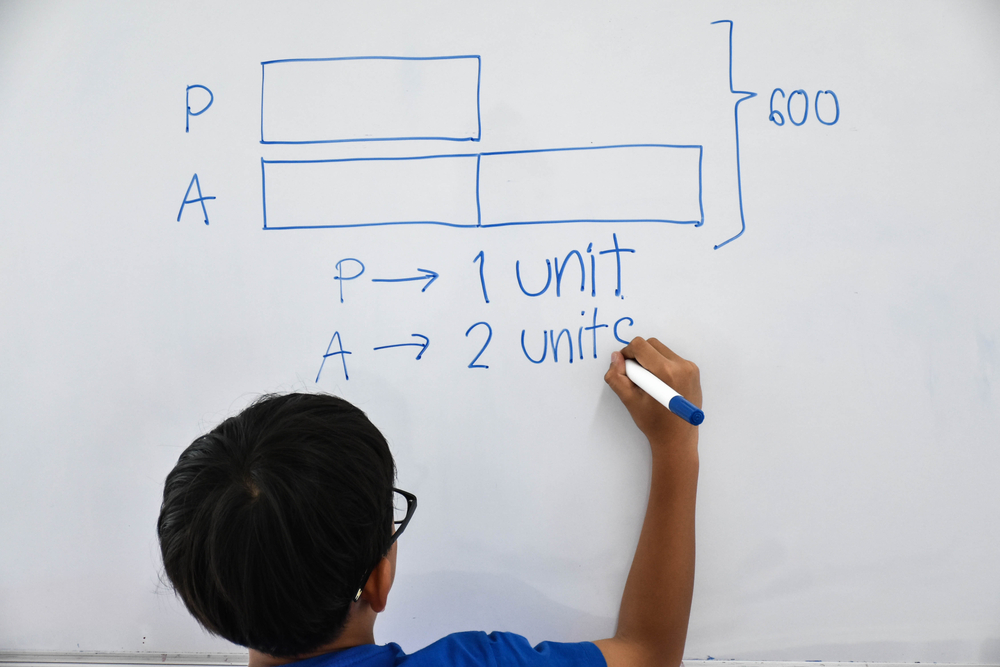
Developing fine motor skills for children aged 3-8 is crucial as these skills are foundational for many everyday activities and are closely linked to cognitive and academic success, especially in mathematics. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, which are necessary for tasks like writing, cutting with scissors, and manipulating small objects. In the context of math, these skills help children perform essential tasks such as holding and using a pencil to write numbers, drawing shapes, handling counting objects, and utilizing math manipulatives like cubes or blocks.
Improving fine motor skills enhances hand-eye coordination and spatial awareness, both vital for understanding geometric concepts and spatial relationships in math. Moreover, as they engage in activities like sorting, threading beads, or fitting pieces into a puzzle, children enhance their problem-solving skills and concentration, fostering a strong foundation for more advanced math concepts.
Parents and teachers should care about developing these skills because children with well-developed fine motor abilities tend to find math tasks more accessible and less frustrating, leading to a more positive attitude towards learning. Early interventions and practice in developing these skills make a lasting impact, setting children on a path of confidence and success in their academic journey and everyday life.


 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students







.jpg)