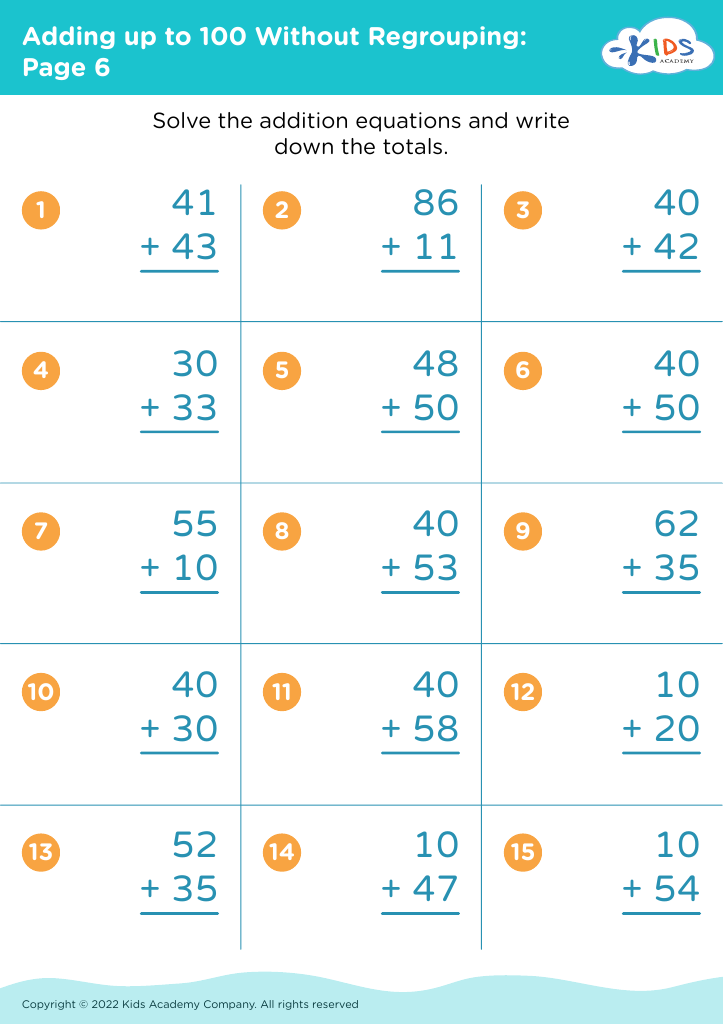
Visual discrimination skills Math Worksheets for Ages 3-8
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's learning experience with our Visual Discrimination Skills Math Worksheets, designed specifically for ages 3-8. These engaging worksheets will help young learners develop essential skills to distinguish between similar shapes, patterns, and numbers, fostering their ability to recognize visual details. Our carefully crafted exercises encourage critical thinking, concentration, and attention to detail while keeping math fun and interactive. With vibrant illustrations and age-appropriate activities, children will sharpen their visual perception and problem-solving skills in a playful environment. Perfect for home or classroom use, these worksheets make mastering math concepts enjoyable and effective for your little ones!
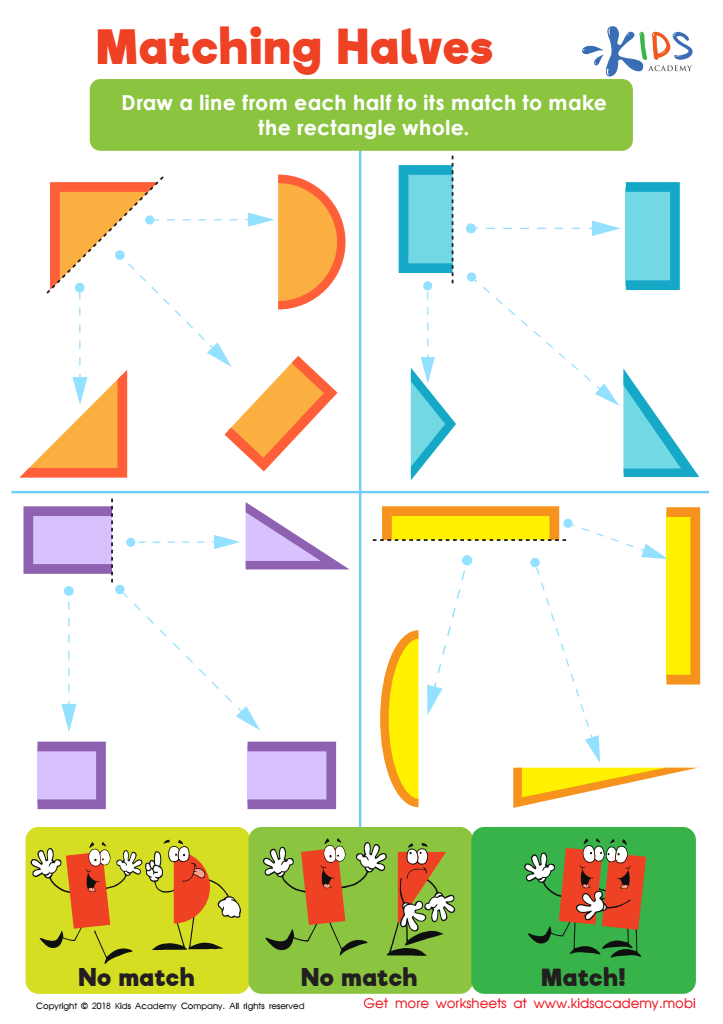

Matching Halves Worksheet
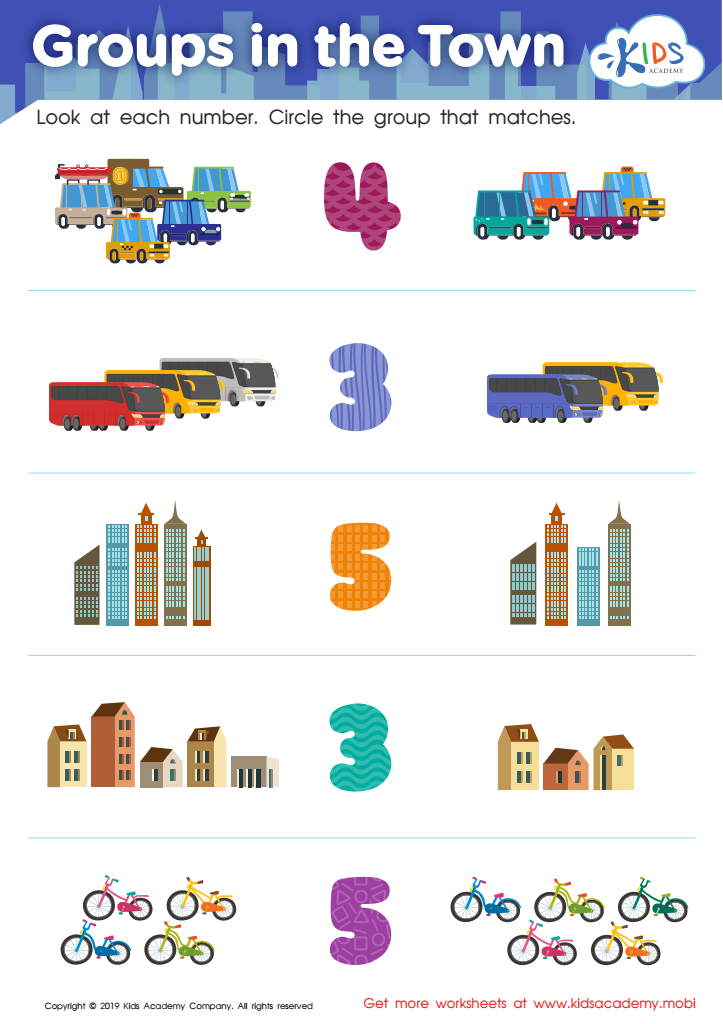

Groups in the Town Worksheet
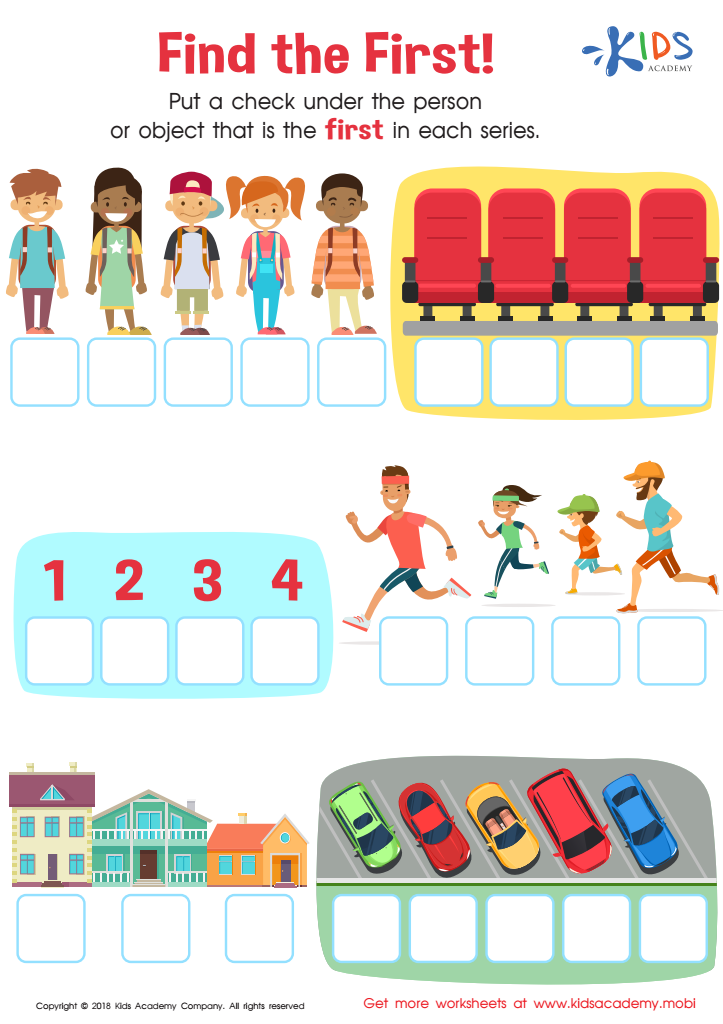

Find the First! Worksheet
Visual discrimination skills are crucial for children aged 3-8, particularly in developing mathematical abilities. These skills refer to the ability to notice similarities and differences in visual information, which forms the basis for recognizing shapes, patterns, and numbers. When children can effectively distinguish between various symbols and numerical forms, they are better equipped to understand fundamental mathematical concepts like counting, addition, and subtraction.
Teachers and parents should be concerned with fostering these skills because they play a significant role in early learning success. Strong visual discrimination enhances a child’s ability to complete puzzles, recognize geometric shapes, and categorize objects—skills that are essential not just in math but in critical thinking and problem-solving across all subjects.
In addition, engaging children in activities that strengthen visual discrimination can build their confidence, making them more enthusiastic learners. Simple exercises, such as sorting objects or playing matching games, can help develop these skills organically. By prioritizing visual discrimination, teachers and parents can lay a strong foundation for productive math learning and support overall cognitive development, preparing children for more complex concepts as they progress through their education.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students