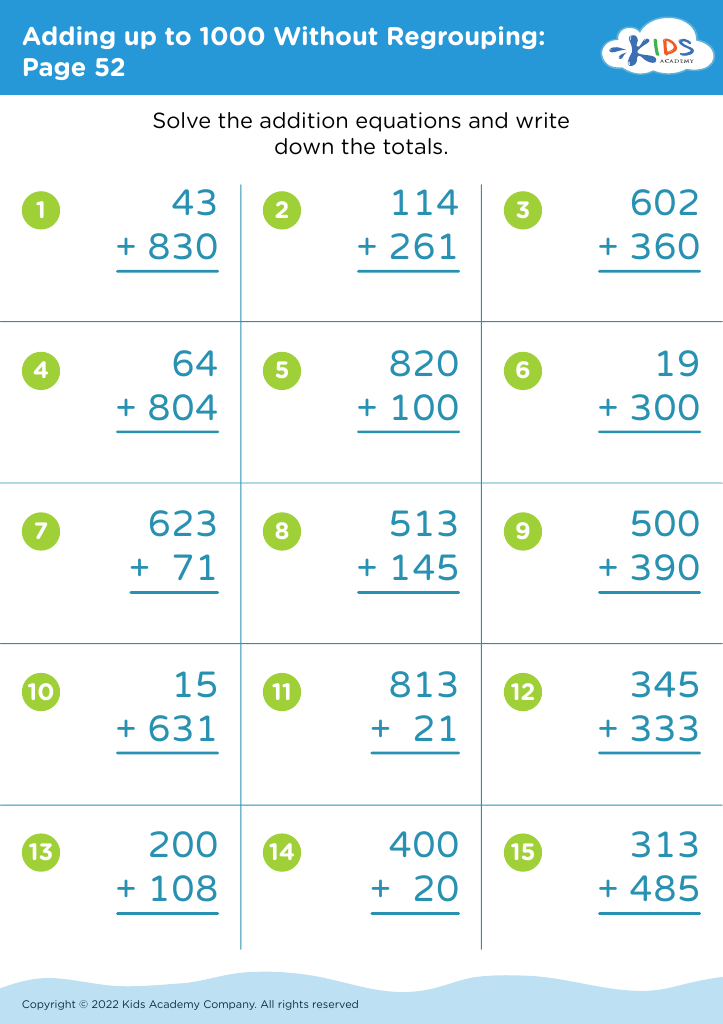
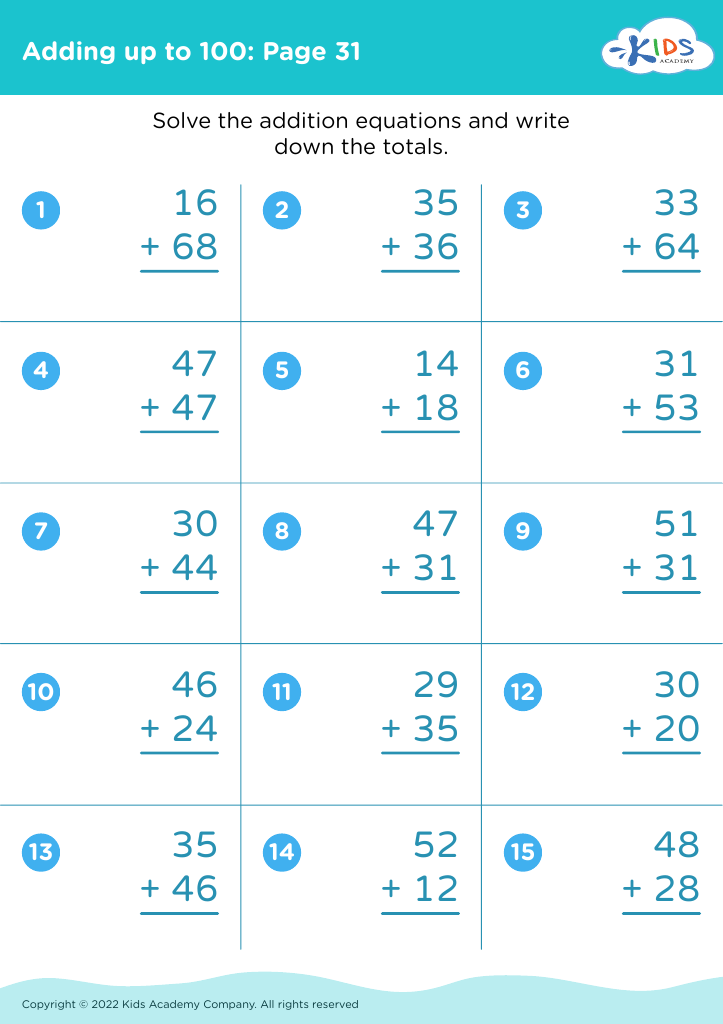
Improve fine motor skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Empower young learners with our "Improve Fine Motor Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 4-8." These specially designed worksheets help children develop fine motor skills while learning basic addition. Each activity blends math practice with essential skills like pencil control, hand-eye coordination, and precision. Perfect for early learners, these engaging worksheets feature fun illustrations and age-appropriate addition problems geared towards enhancing both math fluency and fine motor development simultaneously. Ideal for classroom use or at-home practice, our worksheets make learning addition fun and effective. Give your child the tools to succeed in math and fine motor skills with our expertly crafted resources.
Parents and teachers should care about improving fine motor skills in children aged 4-8 because these skills form the foundation for many essential life activities. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers with the eyes, crucial for tasks such as writing, cutting with scissors, buttoning clothes, and even tying shoelaces. At this age, children's brains are highly adaptable and capable of developing new neural connections that enhance these motor abilities.
By actively focusing on fine motor skill development, parents and teachers can facilitate smoother transitions for children into academic tasks, where precise hand movements are necessary. Improved fine motor skills have been linked to better performance in reading and writing as coordination affects the ability to form letters and comprehend written material. Additionally, enhancing these skills fosters independence, builds confidence, and encourages self-reliance in young children.
Activities such as drawing, beading, or playing with clay also make learning more engaging and enjoyable. In a broader sense, strengthening fine motor skills at a young age contributes to overall brain development, promoting cognitive, social, and emotional growth. Essentially, fine motor development lays the groundwork for academic success and daily life proficiency, making it a vital focus for both parents and educators.







.jpg)