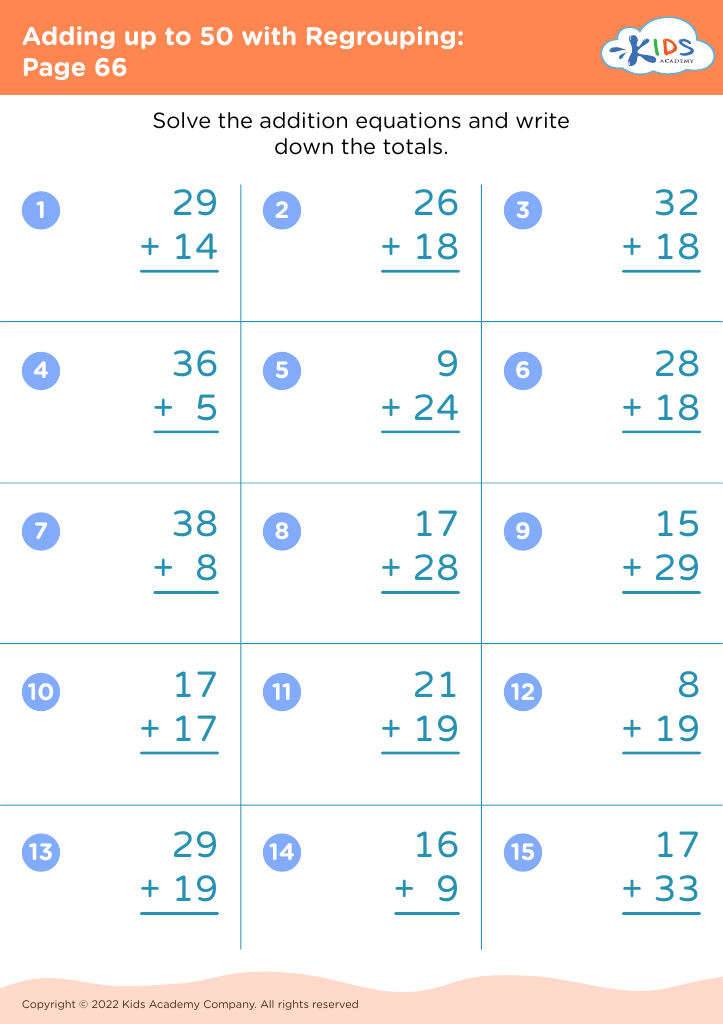
Observation skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 5-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Observation Skills Addition Worksheets for Ages 5-8" balance foundational math with engaging activities to enhance young learners' attention to detail and problem-solving abilities. Designed with vibrant graphics and interactive exercises, these worksheets help children practice basic addition while developing essential observation skills. Perfect for reinforcing in-class learning or as a fun at-home activity, each worksheet invites kids to discover patterns, spot differences, and use critical thinking. The blend of math practice with observational challenges makes learning engaging and effective, ensuring a solid mathematical foundation and improved focus in young students.
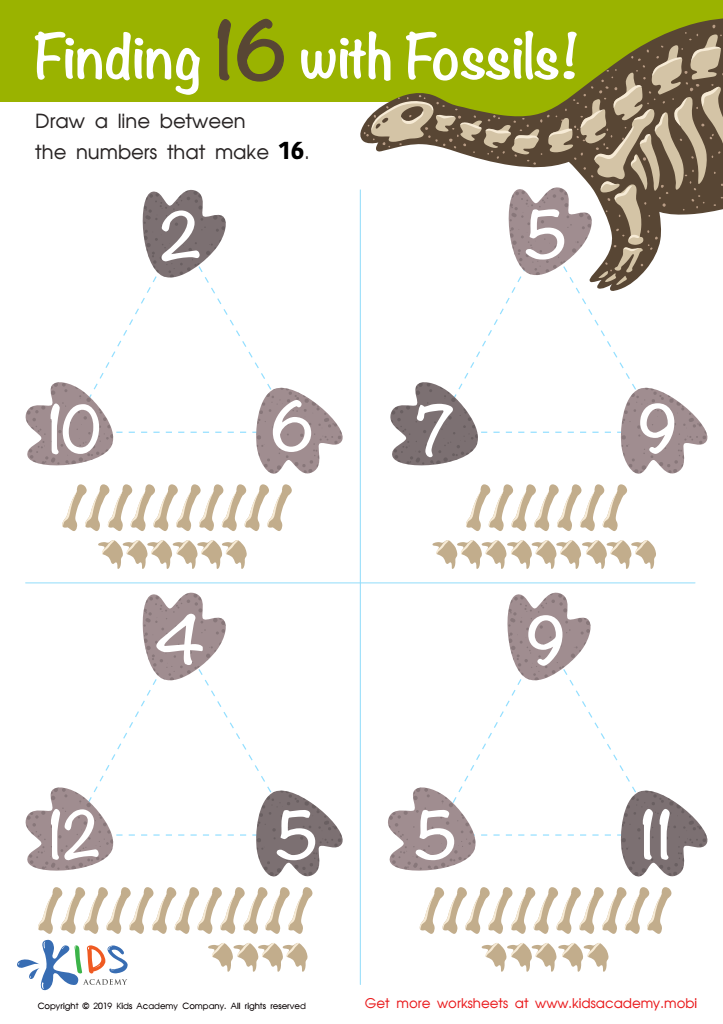

Finding 16 With Fossils Worksheet
Observation skills are critical for young children, aged 5-8, as these formative years are when foundational cognitive and social abilities are developed. Parents and teachers should prioritize enhancing these skills to support holistic development.
Firstly, keen observational abilities enable children to make sense of their environment. By noticing details—colors, shapes, behaviors—kids improve their understanding and retention of information. This lays a groundwork for academic skills including reading, where recognizing letter shapes and patterns is vital.
Secondly, observation fosters curiosity and critical thinking. When children observe and question their world, they engage in scientific thinking, urging them to explore and learn through experience. This curiosity is intrinsic motivation for lifelong learning.
Socially, refined observation enhances empathy. Noticing peers' nonverbal cues—facial expressions, body language—helps children respond appropriately, building stronger relationships and effective communication skills.
Moreover, safety is another consideration. Observant children are more aware of their surroundings, aiding in navigating potentially hazardous situations.
Teachers and parents play a critical role by modeling observant behaviors and creating engaging, detail-rich environments. Activities like nature walks, scavenger hunts, and hands-on experiments can turn observation into enjoyable, habitual practice. This foundational skill shapes not just academic success but emotional intelligence and personal safety, thereby nurturing well-rounded, perceptive individuals.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students