Handwriting Skills Math Worksheets for Ages 5-8
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's handwriting and math skills with our engaging Handwriting Skills Math Worksheets designed specifically for ages 5-8. These worksheets seamlessly integrate handwriting practice with fun math exercises, providing young learners with the opportunity to improve their fine motor skills while solidifying foundational math concepts. Our worksheets cover a variety of topics, from basic addition and subtraction to number recognition, ensuring a comprehensive learning experience. Each page is thoughtfully crafted to keep your child motivated and excited about learning. Explore our collection today and watch your child develop confidence in both handwriting and math abilities! Perfect for home or classroom use.
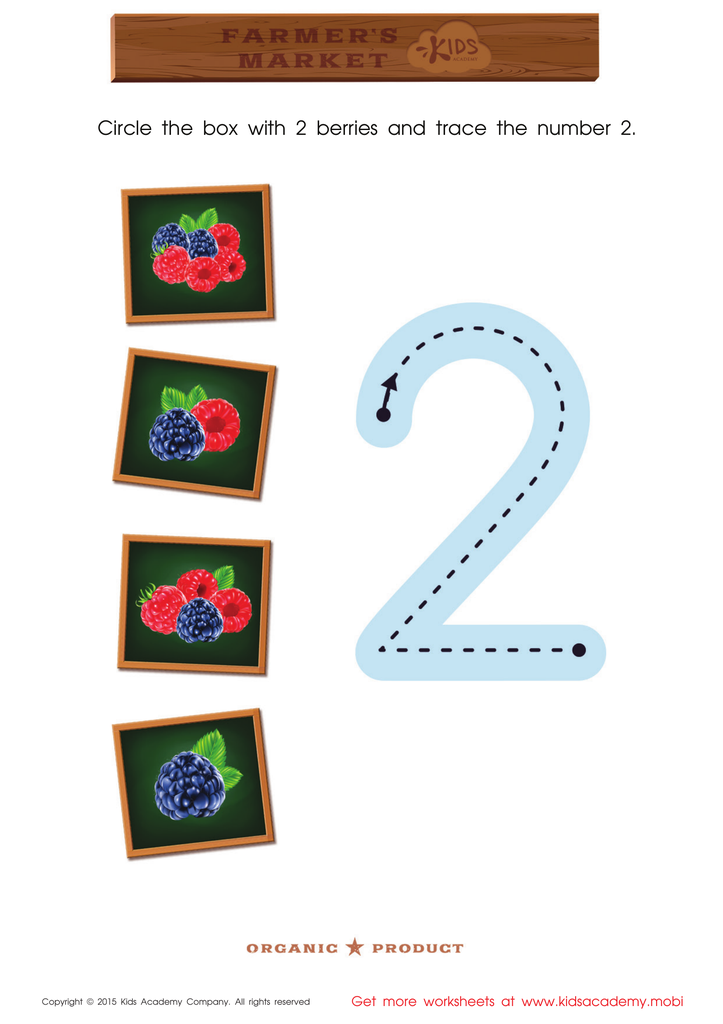


Count the Berries and Trace the Number 2 Printable

Teaching Children to Write Number 4 Worksheet


Kindergarten Number Tracing: Mary's Bag Worksheet


Shapes in Real Life: Cone Worksheet


Number 3 Worksheet


Kindergarten Number Tracing: Medow Flowers Worksheet
Handwriting skills are essential for children aged 5-8, not only in literacy but also in developing mathematical proficiency. During these formative years, kids are beginning to form connections between their written and thought processes. Developing neat and legible handwriting supports their ability to express mathematical concepts clearly. When children can write equations or number forms legibly, they are better able to focus on problem-solving rather than struggling with the mechanics of writing.
Moreover, handwriting practice enhances fine motor skills, which are crucial for overall motor development. These skills are foundational for many everyday tasks and improve hand-eye coordination, which is beneficial in math activities. Additionally, engaging in writing numbers and mathematical symbols can help reinforce number recognition and memorization of math facts, ultimately promoting quicker recall.
Furthermore, handwriting exercises can create discipline and a sense of accomplishment in academic pursuits. When parents and teachers encourage good handwriting, they foster a positive mindset toward learning. Emphasizing handwriting in math feels real to children and showcases that math extends beyond mere calculation; it is linked to clear communication and organization of ideas. By prioritizing these skills, adults can better prepare children for success in academics and develop confidence in their abilities.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students




















