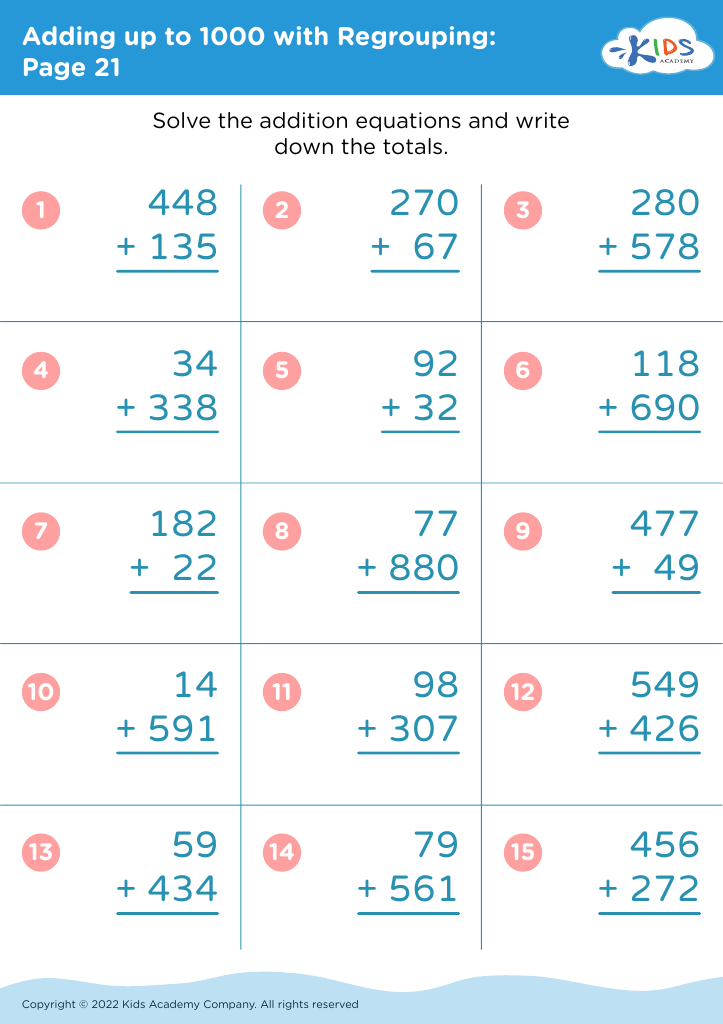
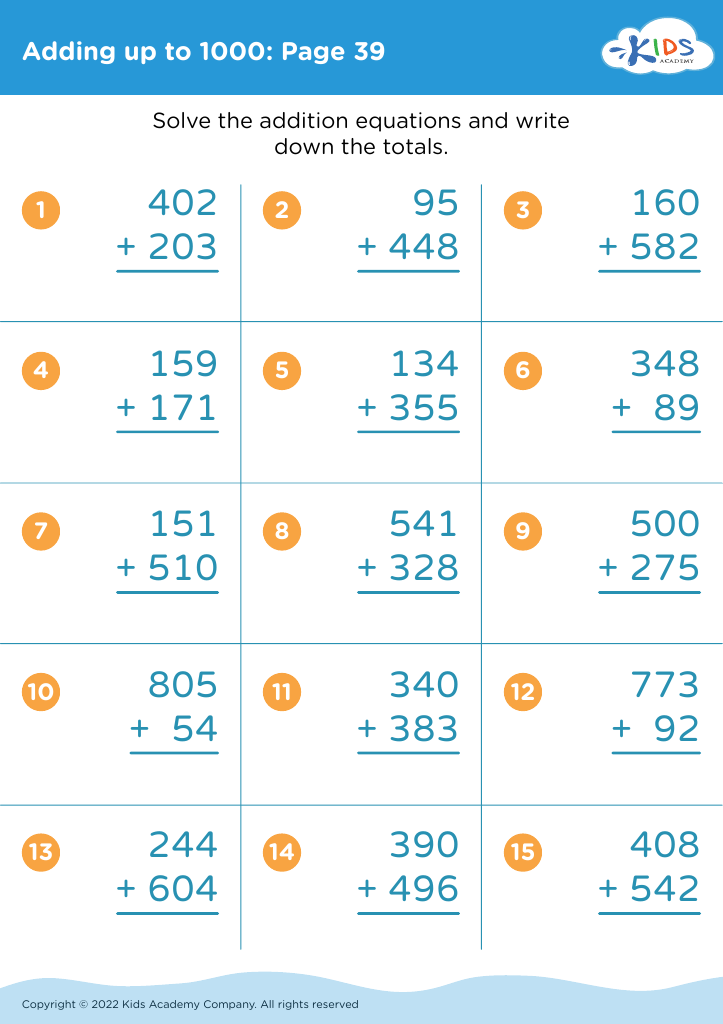
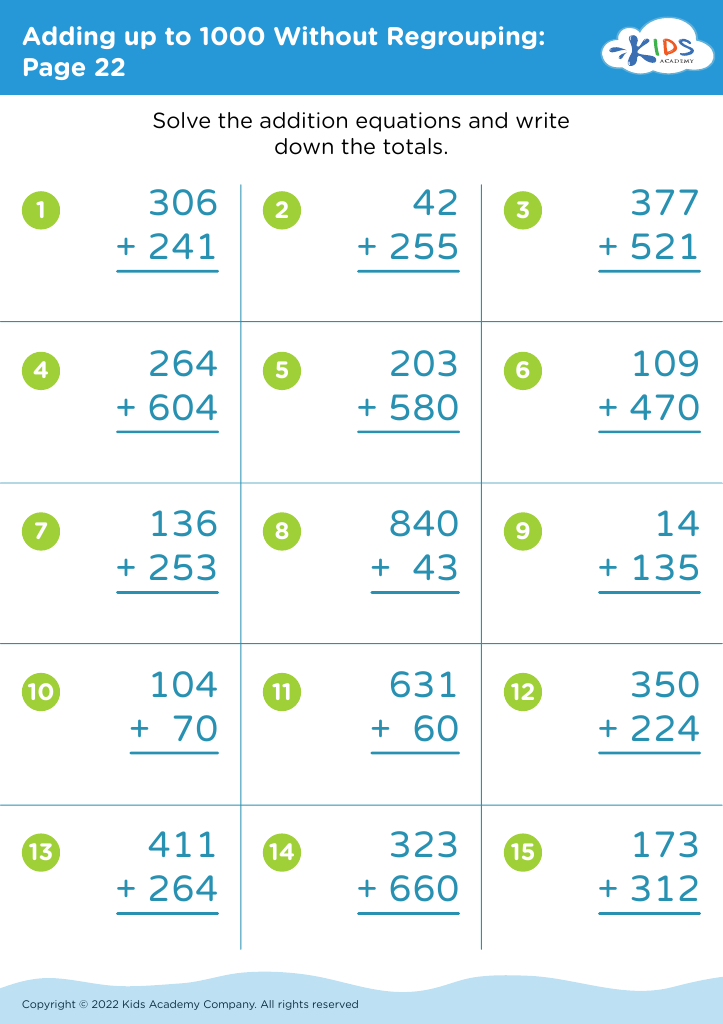
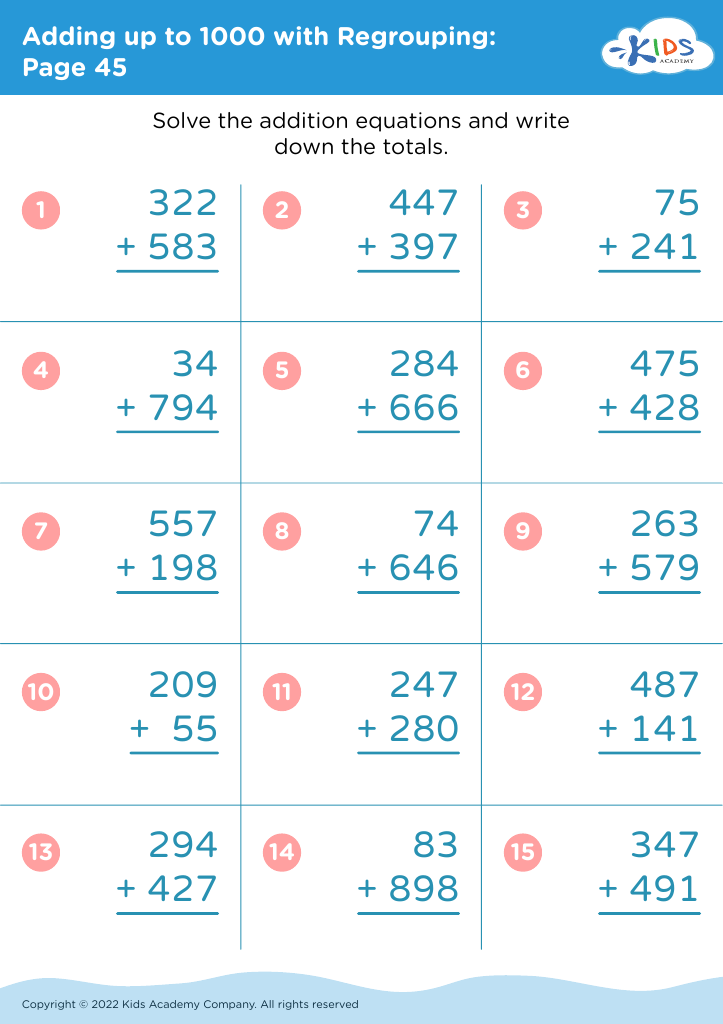
Fine motor skills (writing) Adding up to 1000 Worksheets for Ages 6-7
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills and writing capabilities with our "Adding Up to 1000" worksheets, specifically designed for ages 6-7. These engaging activities not only promote mathematical understanding but also focus on developing essential writing skills through practice. Each worksheet is crafted to help young learners refine their hand-eye coordination, control, and dexterity while adding numbers up to 1000. With fun illustrations and diverse exercises, children will stay motivated as they improve their fine motor skills. Empower your child’s learning journey and watch them thrive in math and writing through these interactive, educational resources! Explore our collection today!
Fine motor skills are essential for children aged 6-7 as they provide the foundation for various tasks in both academic and daily life. In this critical developmental stage, fine motor skills, particularly writing, play a significant role in a child's ability to express themselves, communicate ideas clearly, and engage in learning activities effectively. Mastering fine motor skills enables children to hold pencils correctly, form letters, and write legibly, which are crucial for success in school.
Parents and teachers should care about fine motor skills because they directly influence academic performance and self-esteem. A child who struggles with writing may feel frustrated and discouraged, potentially leading to a negative attitude toward learning. Furthermore, fine motor skills are not limited to writing but extend to other activities such as tying shoelaces, buttoning shirts, and using scissors—all important life skills.
Encouraging activities like drawing, coloring, and playing with building blocks helps strengthen fine motor development. Ultimately, supporting fine motor skills not only enhances children's writing abilities but also lays the groundwork for future tasks and fosters independence, confidence, and a love for learning. By prioritizing fine motor skill development, parents and teachers can significantly impact children's overall growth and academic success.