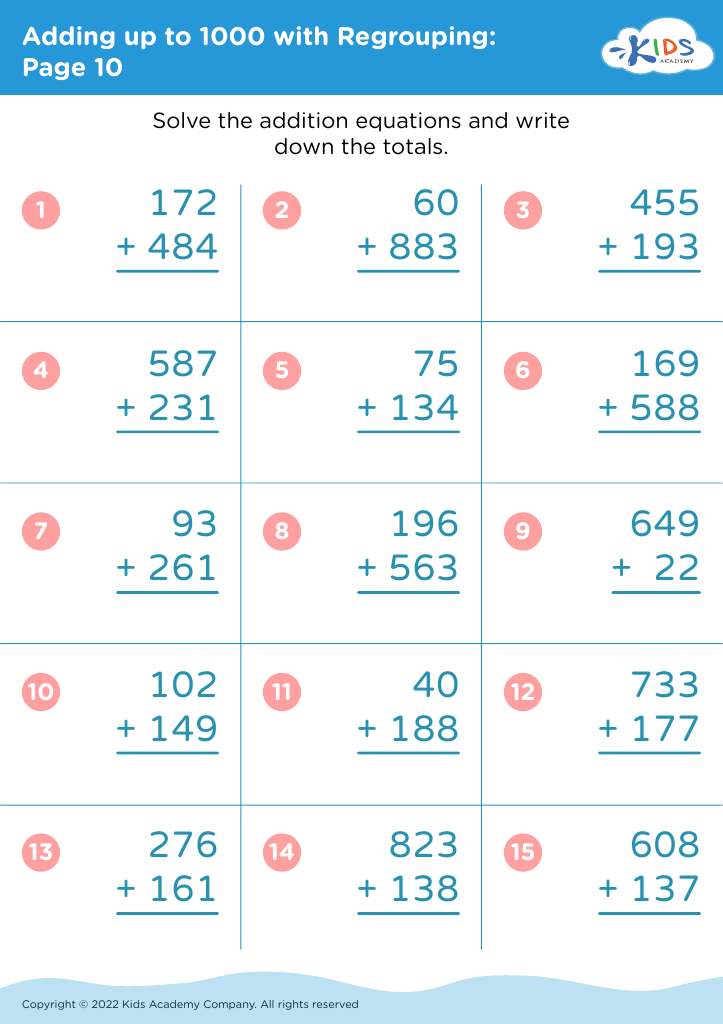
Developing fine motor skills Math Worksheets for Ages 6-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
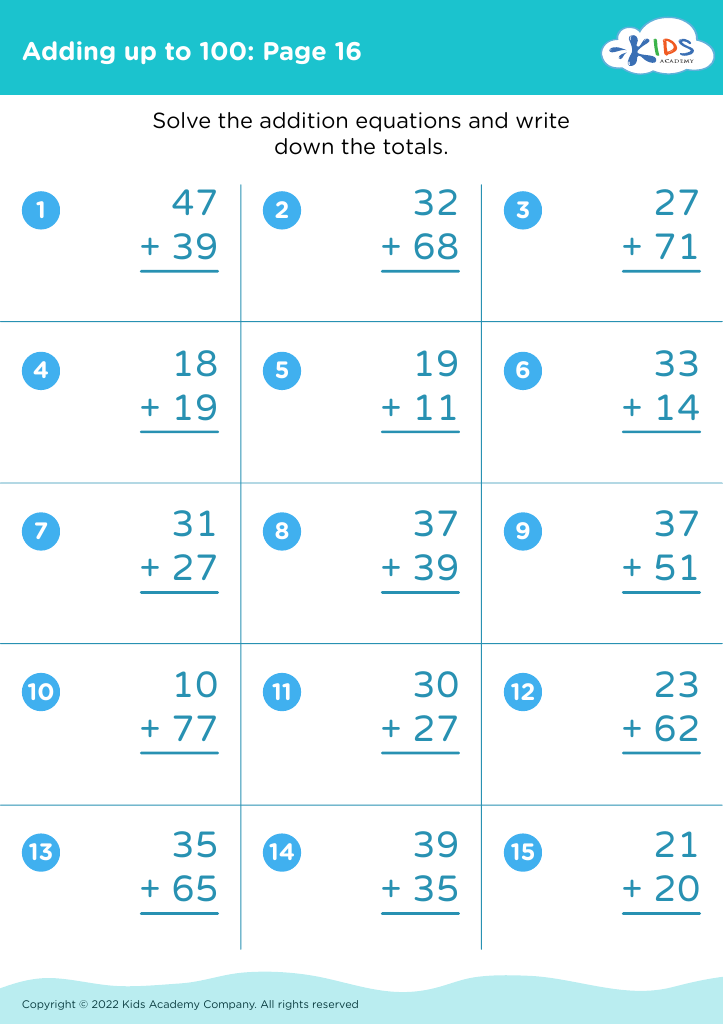
Enhance your child's fine motor skills with our engaging math worksheets designed specifically for ages 6-7. These worksheets combine foundational math concepts with fun, interactive activities that encourage children to practice essential skills like hand-eye coordination, tracing, and writing. By integrating fine motor skill development with mathematics, our resources support early learners in becoming more confident as they refine their coordination while solving problems. Ideal for classrooms or at-home learning, these worksheets prepare children for future academic success while keeping them entertained. Explore our collection today and watch as your young learners thrive!
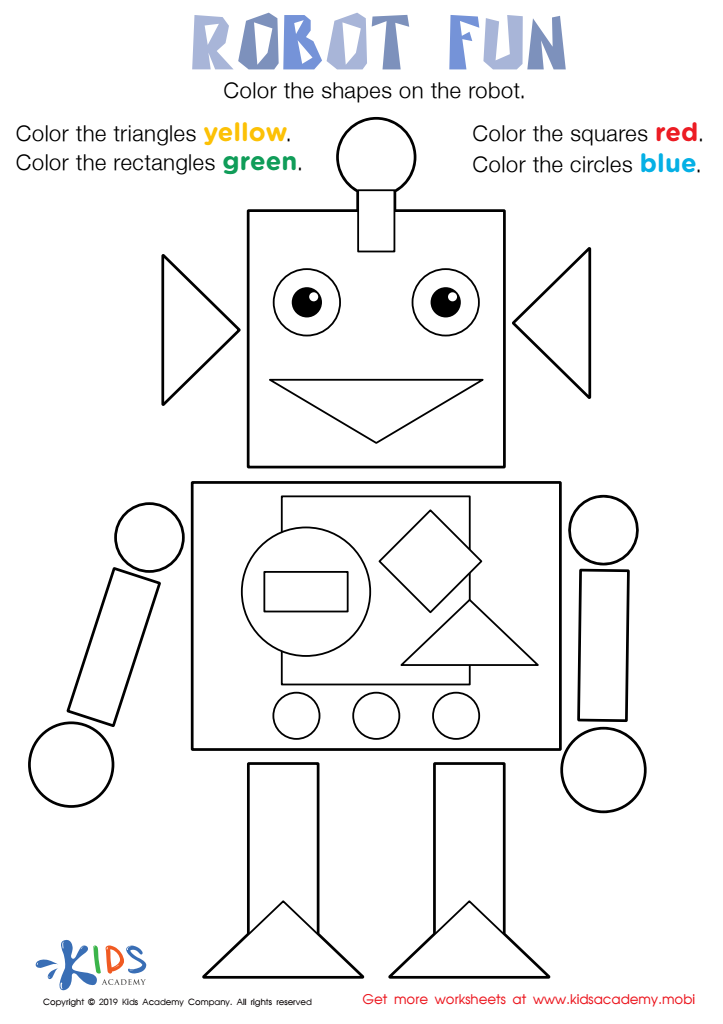

Robot Fun Worksheet
Developing fine motor skills in children aged 6-7 is crucial for their overall growth, especially in the realm of mathematics. Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscle movements, allowing children to execute precise tasks. When children master these skills, they can engage more effectively in activities such as writing numbers, drawing shapes, and manipulating math tools, all of which are foundational for mathematical understanding.
For teachers and parents, encouraging fine motor development fosters confidence in children. A child who can grip a pencil properly and form numbers neatly is more likely to participate actively in math activities. This skill also correlates with better problem-solving abilities, as children can physically manipulate objects (like counting blocks or money) to grasp abstract concepts.
Moreover, developing fine motor skills helps enhance a child's concentration and perseverance, qualities that are essential for academic success. Engaging in activities such as cutting, pasting, or crafting provides a dual benefit: reinforcing fine motor skills while making math fun and interactive. By supporting fine motor development, parents and teachers can lay a strong foundation for children’s mathematical journey, making learning enjoyable and preparing them for more complex skills in the future.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students