Problem-Solving Skills Skip Counting Worksheets for Ages 6-7
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child’s problem-solving abilities with our Skip Counting Worksheets tailored for ages 6-7. Our carefully designed exercises help young learners build essential math skills by practicing counting by 2s, 5s, and 10s. Not only do these worksheets strengthen counting fluency, but they also develop critical thinking and problem-solving capabilities. With engaging and fun activities, your child will enjoy learning and improving their number sense. Perfect for both classroom and at-home practice, these worksheets provide a foundation for future math successes. Start your child's mathematical journey today with our dynamic and educational Skip Counting Worksheets!
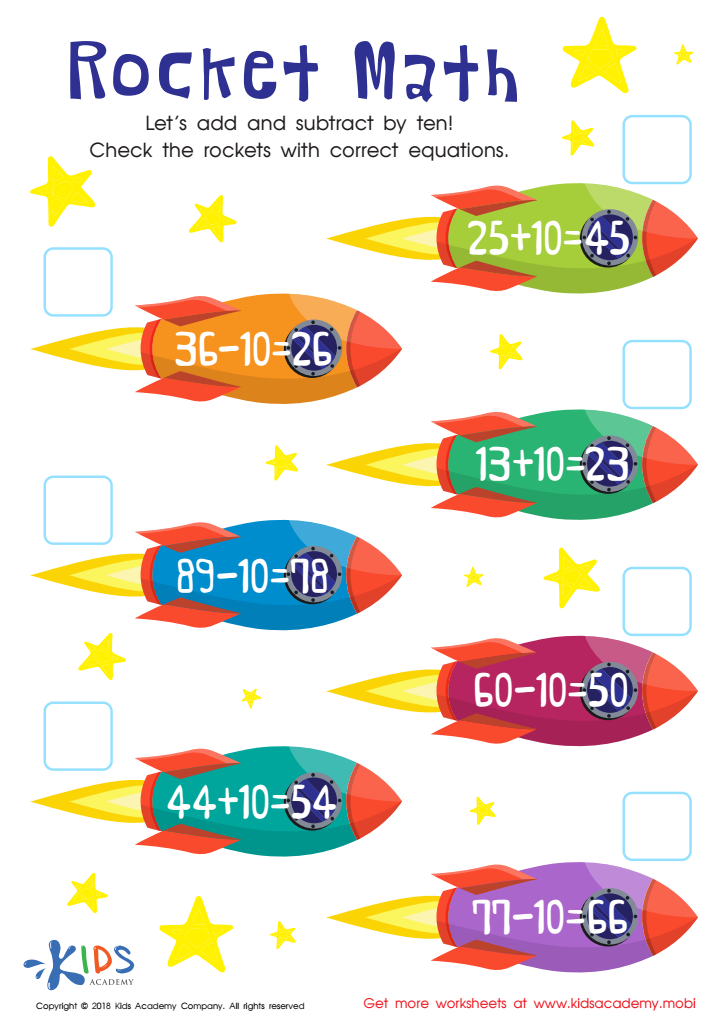

Rocket Math Worksheet
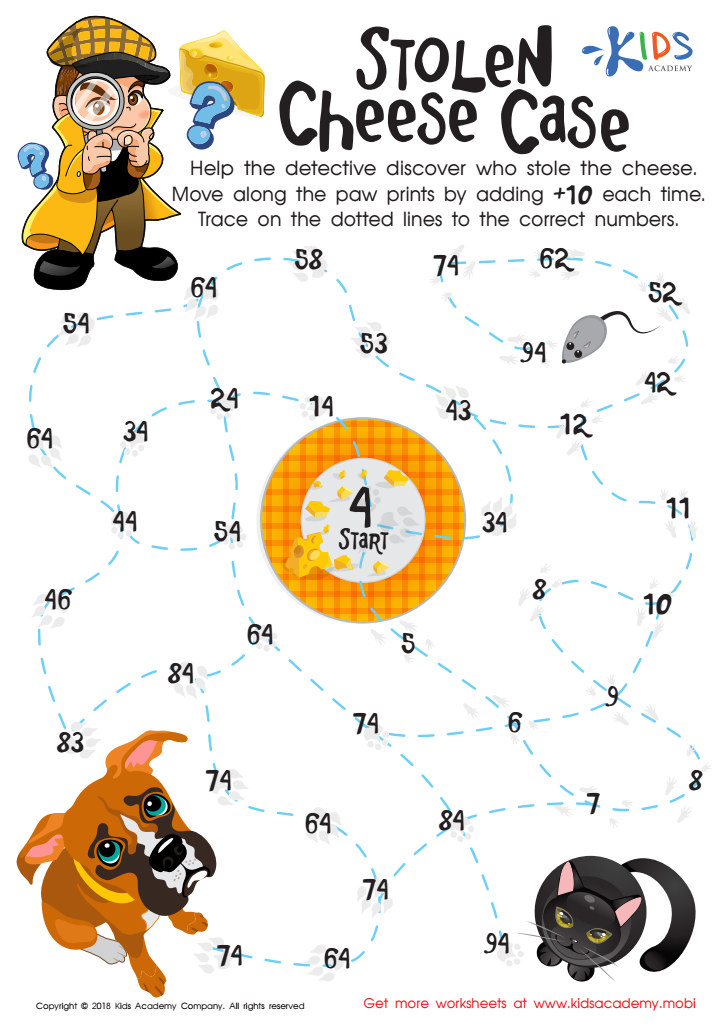

Stolen Cheese Case Maze Worksheet


Skip Counting by 5s: Outer Space Math Printable
Developing problem-solving skills through skip counting is essential for children aged 6-7 as it lays a strong foundation for future mathematical understanding. At this young age, children are naturally curious and enthusiastic about learning, making it an ideal time to introduce vital concepts in a fun, approachable way. Skip counting, essentially counting forward by numbers other than one (e.g., by 2s, 5s, or 10s), helps children build numerical fluency and recognize patterns in numbers.
For parents and teachers, incorporating skip counting into learning is crucial because it supports the development of more complex mathematical operations such as multiplication and division. When children practice skip counting, they become familiar with number sequences and internalize the relationships between numbers, which enhances their ability to solve arithmetic problems more effectively.
Moreover, incorporating skip counting cultivates critical thinking and concentration. As they identify and extend patterns, children improve their logical reasoning abilities, which are applicable to broader problem-solving contexts both inside and outside the classroom.
Finally, making skip counting a regular practice through engaging activities or games ensures that learning remains enjoyable. This minimizes anxiety around math and fosters a positive attitude toward the subject, encouraging continuous growth and interest in mathematics. Therefore, for robust cognitive and academic development in young learners, a focus on skip counting and problem-solving skills is indispensable.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students
















