Basic arithmetic skills Adding up to 100 Worksheets for Ages 6-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Introducing our "Basic Arithmetic Skills: Adding Up to 100 Worksheets" designed specifically for children ages 6 to 8! These engaging worksheets focus on helping young learners master essential addition skills while making math fun and accessible. With various exercises that progress in difficulty, students will learn to add numbers effectively and confidently work towards their goals. These resources not only reinforce addition concepts but also enhance problem-solving skills and number recognition. Perfect for classroom use or at-home practice, these worksheets are an invaluable tool for early education. Help your child build a strong foundation in math with our comprehensive worksheets today!
Basic arithmetic skills, particularly adding up to 100, are essential for children aged 6-8 as they form the foundation for lifelong mathematical understanding. At this critical developmental stage, children are learning to grasp numbers and their relationships. Mastering addition not only enables them to solve everyday problems, like figuring out how many items they have in total, but also boosts their confidence in handling more complex math later on.
Parents and teachers play a vital role in nurturing these skills, as early experiences with math impact a child's attitude towards the subject. By fostering a solid grasp of basic addition, children enhance their cognitive abilities, become better problem-solvers, and improve their critical thinking skills. Such foundational knowledge can also contribute to improved performance in other subjects, including science and technology, promoting interdisciplinary learning.
Moreover, proficiency in basic arithmetic supports important life skills, helping children develop budgeting skills in later life and making educated decisions. Encouraging children to practice adding up to 100 through engaging activities makes learning enjoyable and relevant. By prioritizing these skills, parents and teachers can help pave the way for students to thrive in school and beyond, ensuring their future academic success.

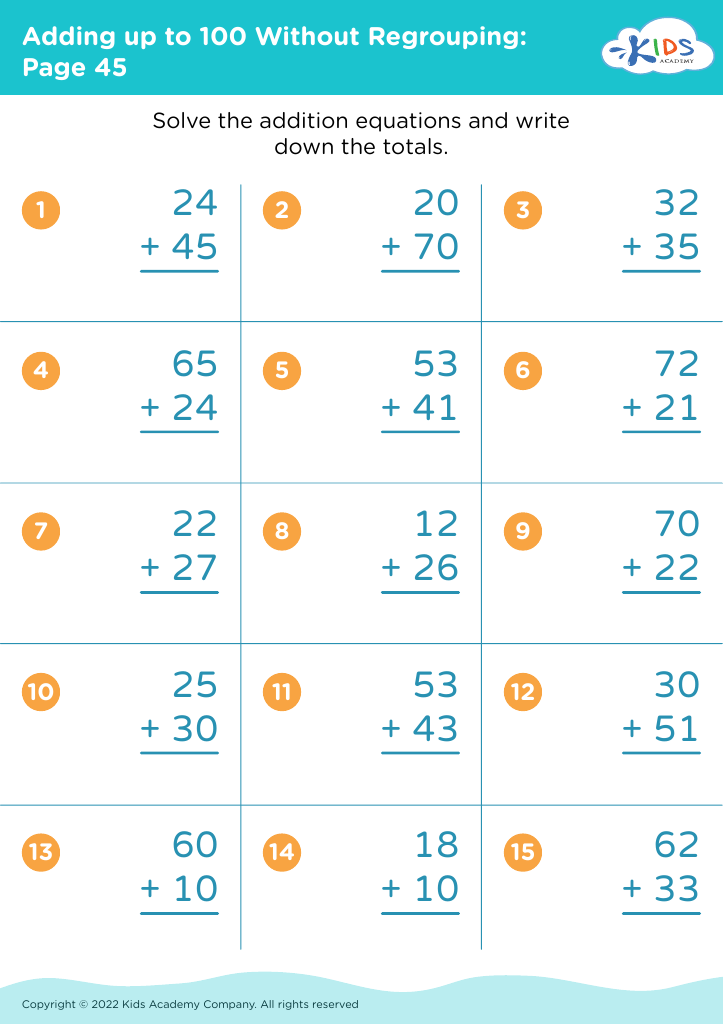
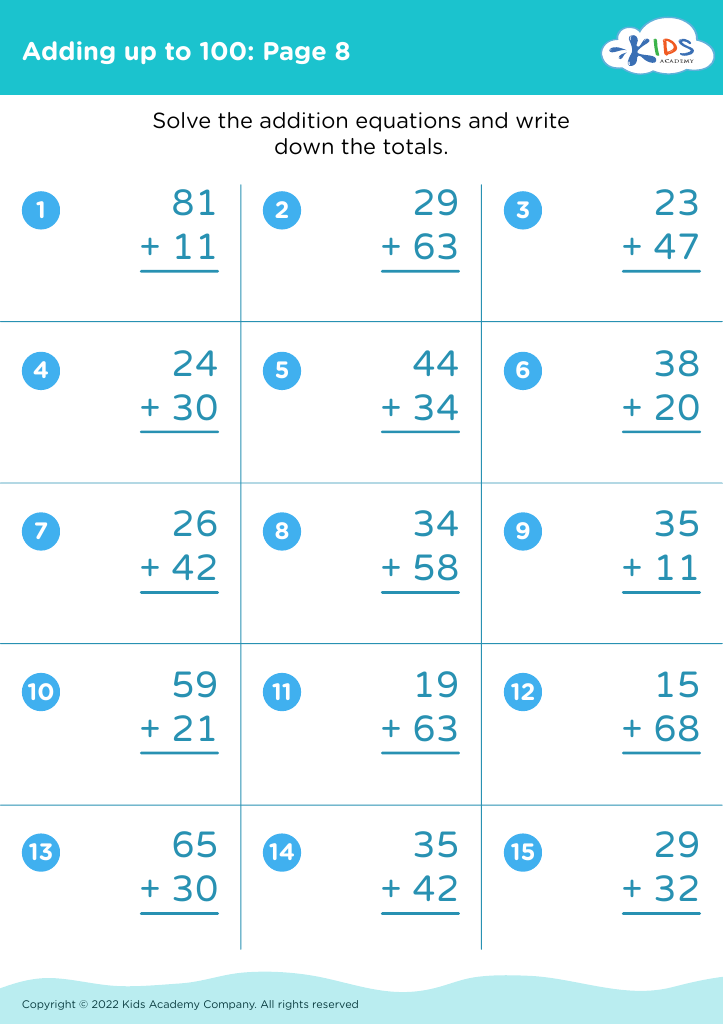
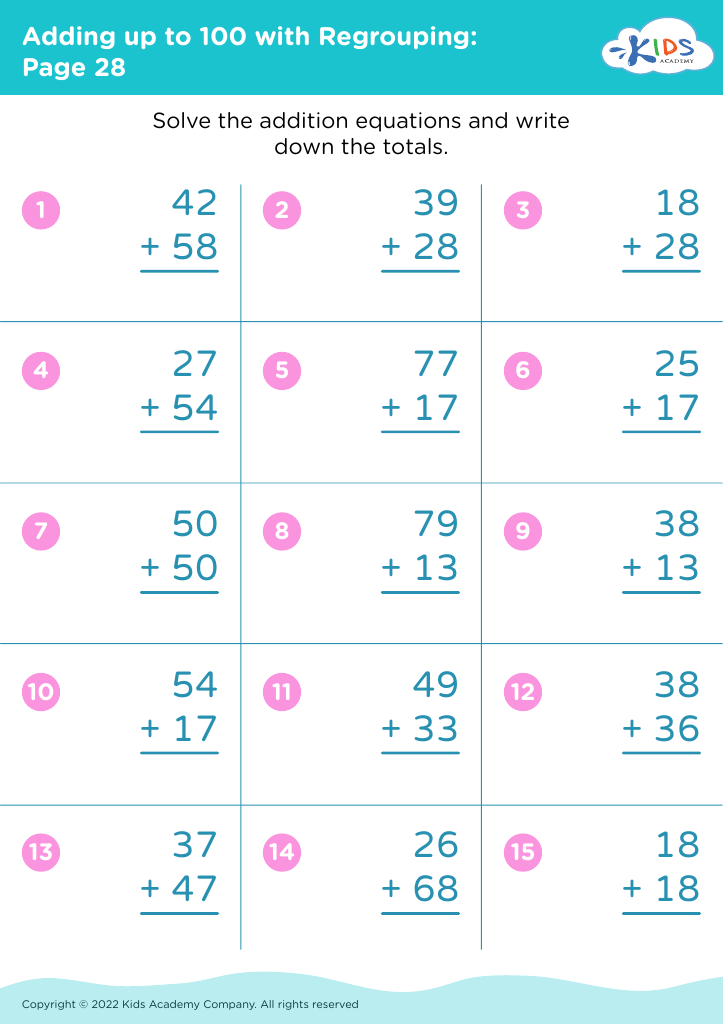


%20(1).jpg)











