Practice writing numbers Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 6-8
6 filtered results
-
From - To
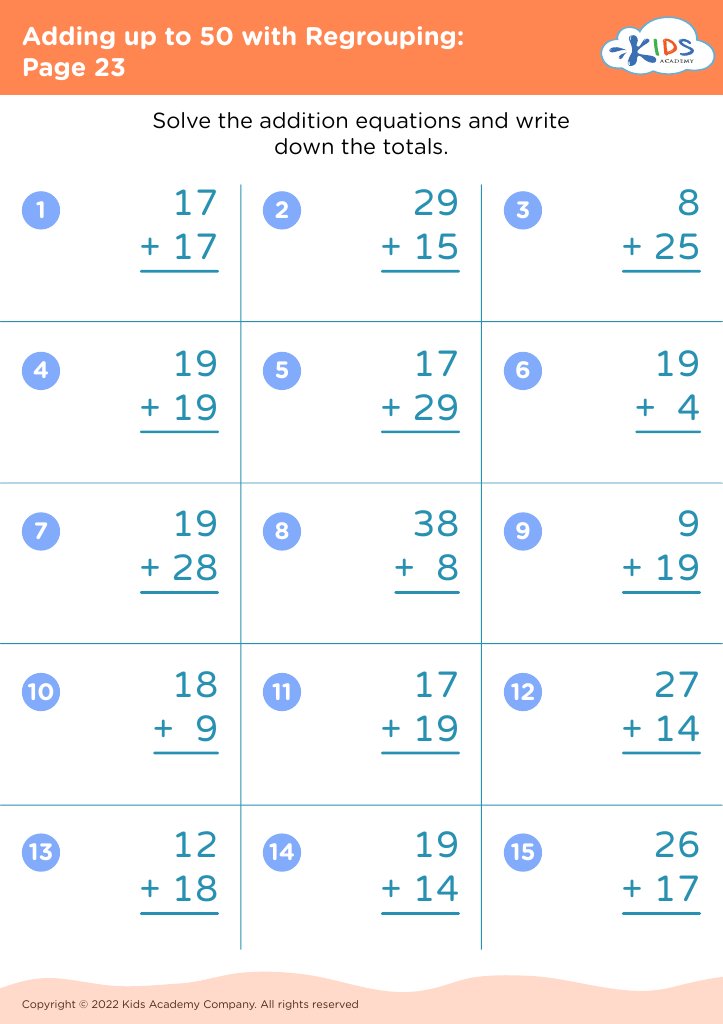
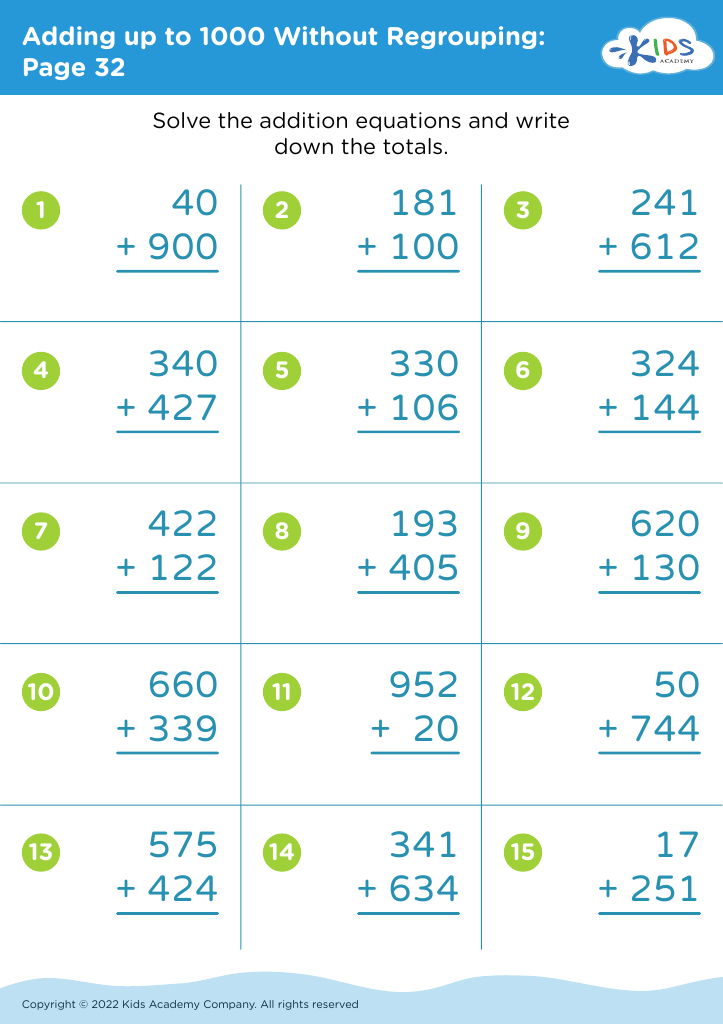
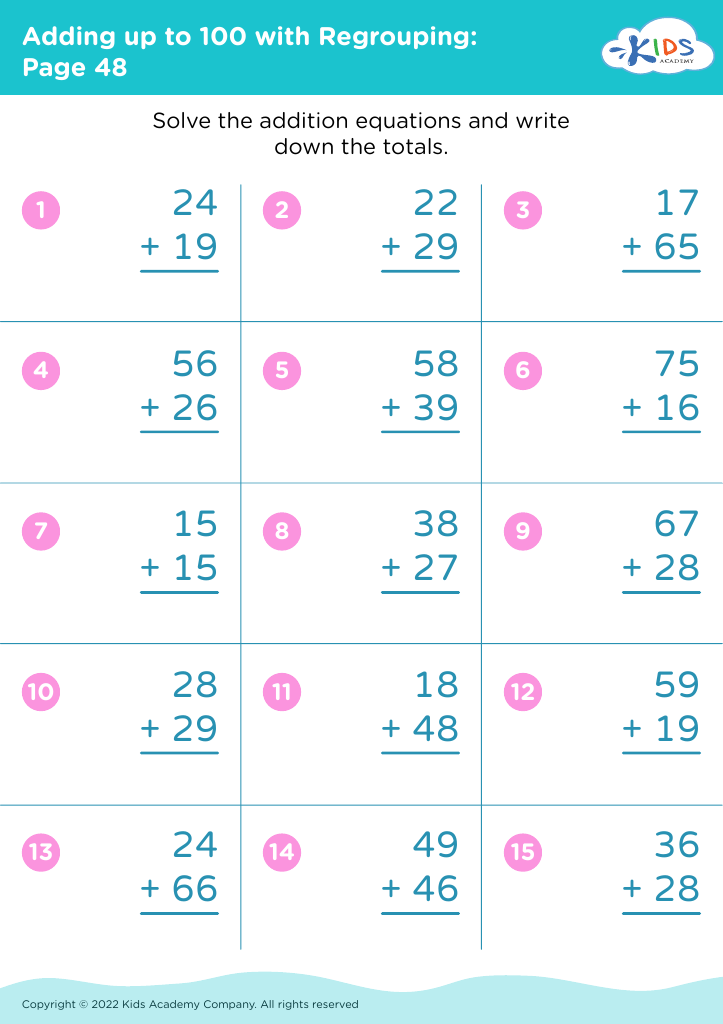
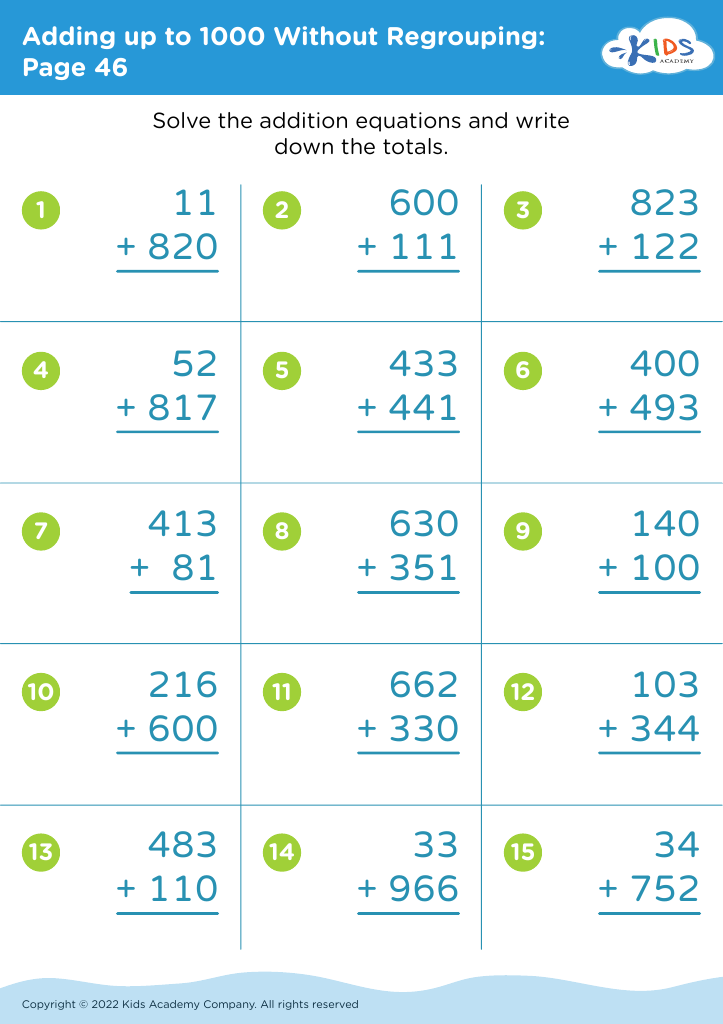
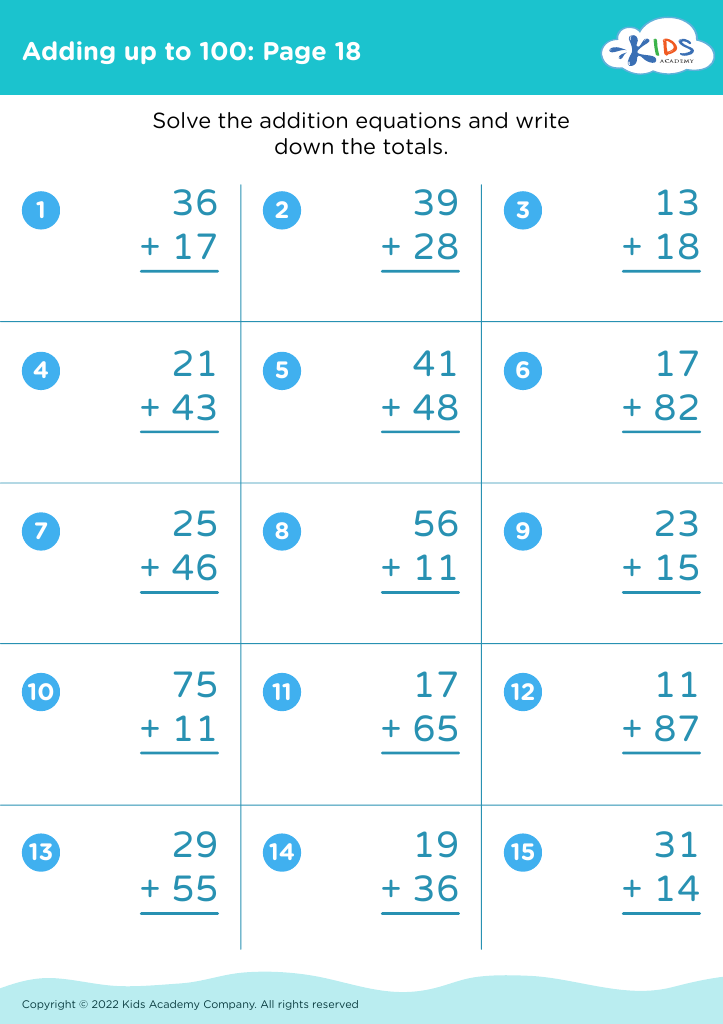
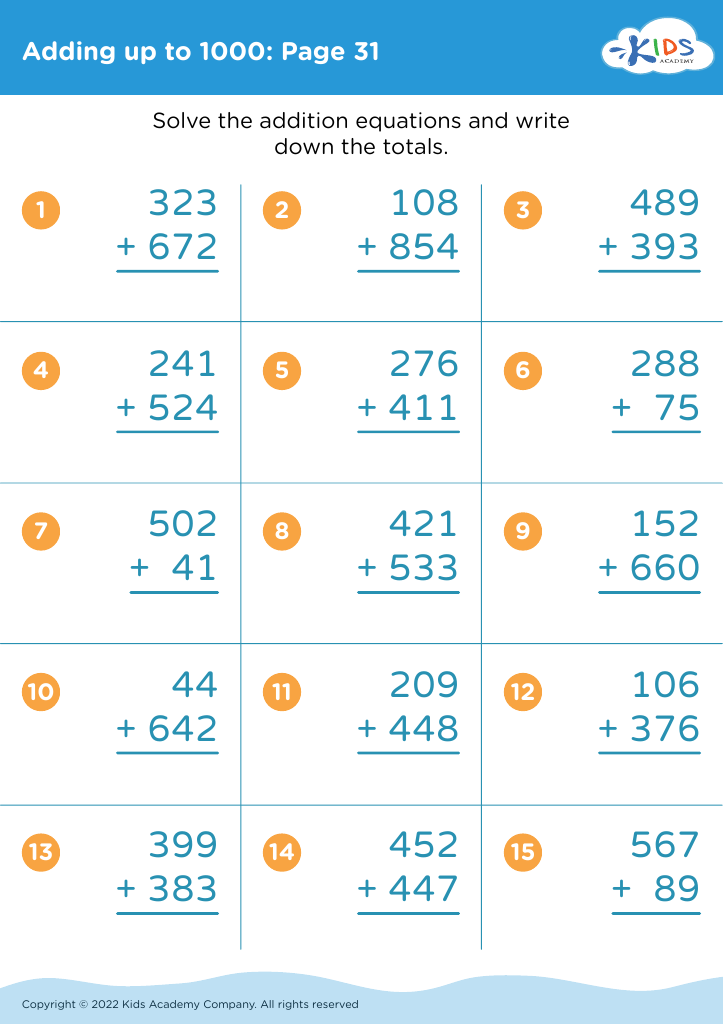
Introduce your young learners, aged 6-8, to our engaging "Practice Writing Numbers Addition & Subtraction Worksheets." These worksheets are tailor-made to assist in developing essential math skills by combining basic arithmetic operations with number writing practice. Each worksheet challenges students to solve simple addition and subtraction problems, reinforcing number recognition, sequencing, and fine motor skills. Designed by Kids Academy, our printable resources aim to make learning fun and effective for children. Ideal for both classroom and home use, these worksheets set the foundation for math proficiency while enhancing problem-solving abilities. Start your kids on the path to math success today!
Parents and teachers should care about practice writing numbers, addition, and subtraction for children aged 6-8 because these foundational math skills are critical for overall cognitive development and future academic success. At this age, children are in a pivotal stage where they begin to formalize their understanding of numbers and basic arithmetic operations, which are essential building blocks for more complex mathematical concepts later on.
First, practicing writing numbers enhances fine motor skills and strengthens number recognition, aiding children in accurately interpreting and using numerical data in various contexts. Mastery of addition and subtraction introduces children to logical thinking and problem-solving, promoting mental arithmetic abilities that support everyday tasks and more advanced educational challenges.
Second, early competency in these areas boosts children's confidence. When children find success with basic math problems, it fosters a positive attitude towards learning and encourages perseverance. This positive reinforcement at a young age lays the groundwork for a proactive approach towards education in the future.
Lastly, early and consistent practice in math ensures that gaps in understanding are identified and addressed promptly. Educators and parents can provide targeted support, thereby preventing math-related anxiety and closing potential achievement gaps. This comprehensive development fosters resilience and adaptability, preparing children for higher educational endeavors and real-world applications.