Event sequencing History Worksheets for Ages 6-8
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover our engaging Event Sequencing History Worksheets designed specifically for children ages 6-8! These worksheets help young learners grasp the concept of chronological order and develop critical thinking skills by arranging historical events accurately. With vibrant designs and kid-friendly language, children will explore significant milestones in history while revisiting key events that shaped our world. Perfect for home or classroom use, these worksheets encourage discussion and reflection on past events. Foster your child's understanding of history as they practice sequencing and enhance their reading comprehension with our fun, educational resources! Start your child's historical journey today!
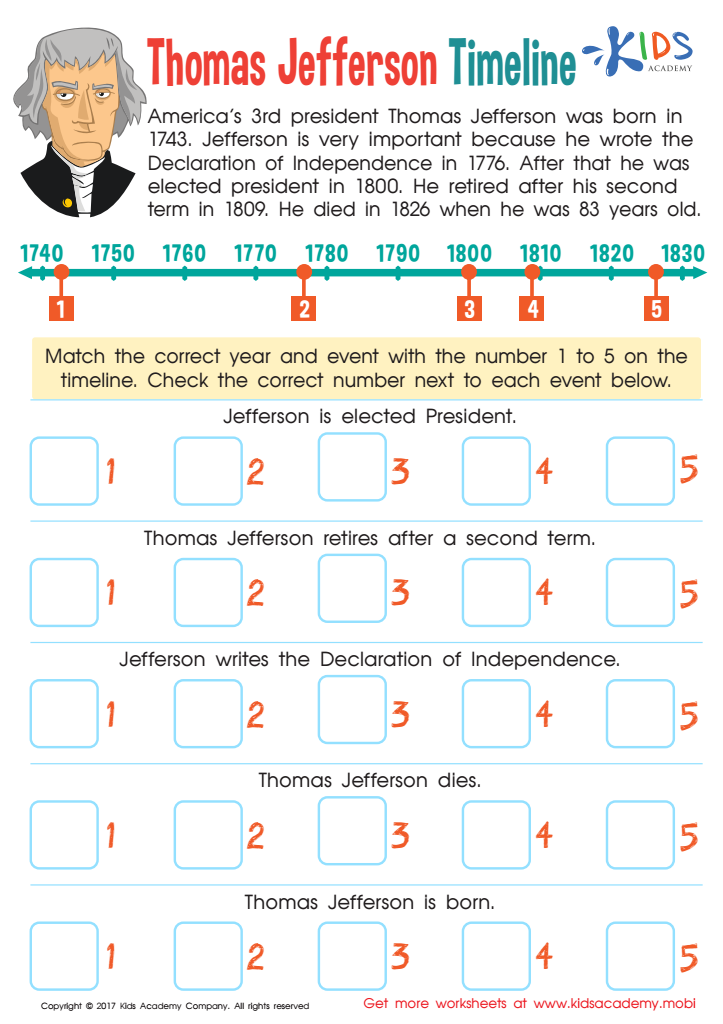

Thomas Jefferson Timeline Worksheet
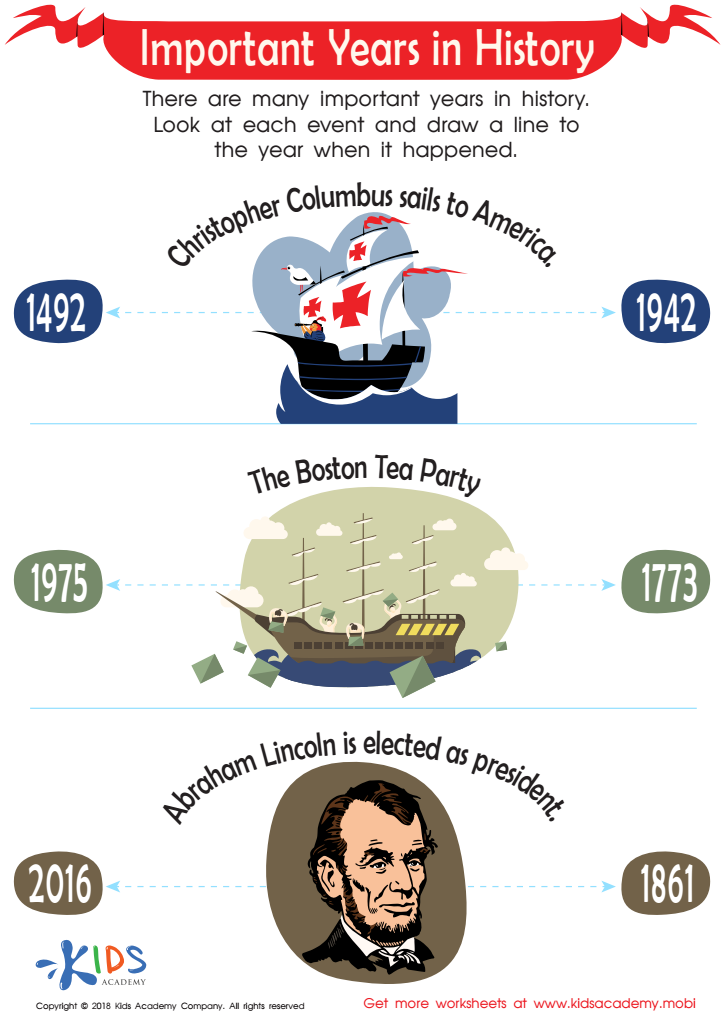

Important Years in History Worksheet


George Washington Timeline Worksheet
Event sequencing is a fundamental skill for children aged 6-8 that enhances their understanding of narratives and real-life situations. This skill contributes significantly to cognitive development, helping children grasp cause-and-effect relationships, which is essential not only in language arts but also in subjects like math and science.
Parents and teachers should care about event sequencing as it lays the groundwork for critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. When children learn to order events, they improve their comprehension skills, enabling them to follow stories better and communicate their own ideas more clearly. Sequencing activities, such as storytelling, organizing daily routines, or crafting timelines, promote engagement and foster creativity.
Moreover, event sequencing assists in enhancing memory and recall, vital for academic success. Children learn to remember key details and events, which is crucial during assessments and standardized tests. Promoting sequencing activities in the classroom and at home also strengthens collaboration and communication among peers, as they discuss and share their thoughts.
In summary, understanding event sequencing is essential for cognitive and linguistic development in children aged 6-8, making it a crucial focus for both parents and educators. By prioritizing this skill, adults can help children become more competent and confident learners.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students