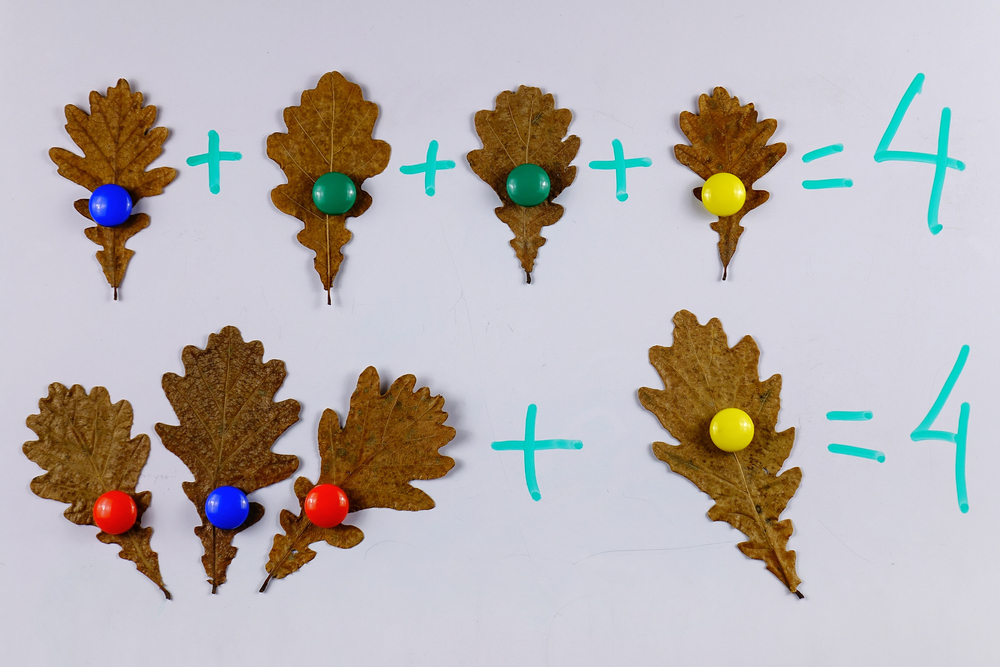
Understanding division Addition Worksheets for Ages 6-9
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Discover engaging "Understanding Division Addition Worksheets" designed for ages 6-9. Our dynamic resources make learning fun and effective, transforming abstract division concepts into comprehensible tasks for young minds. Each worksheet gradually introduces division through familiar addition exercises, reinforcing foundational math skills in a simple and approachable manner. Support your child’s academic journey with tailored exercises that build confidence, emphasize critical thinking, and promote problem-solving abilities. Visit Kids Academy to enhance your child's math comprehension and develop essential skills that pave the way for future success within a supportive and enjoyable learning environment.
Parents and teachers should understand and care about teaching division and addition to children aged 6-9 because these fundamental math concepts form the building blocks for more advanced mathematics and critical thinking skills. During these formative years, children are especially receptive to learning new concepts that can shape their cognitive development. By grasping addition, students develop skills in counting, combining groups, and understanding positive increments, allowing them to efficiently manage basic arithmetic operations required in daily life.
Introducing division helps children comprehend how larger groups can be evenly split into smaller, manageable parts, which is vital for problem-solving and logical reasoning. Both these concepts cultivate a child’s numerical fluency and boost their confidence in handling numbers. Mastery of such skills at an early age promotes a positive attitude towards mathematics, easing future transitions to more complex topics like fractions, algebra, and beyond.
Moreover, understanding these skills goes beyond academics; they’re essential for practical tasks such as sharing, budgeting, and time management. A solid foundation in basic arithmetic enables children to tackle real-world problems more effectively. Ultimately, by equipping students with strong mathematical foundations, parents and teachers help ensure that children develop into capable, independent thinkers who enjoy lifelong learning.
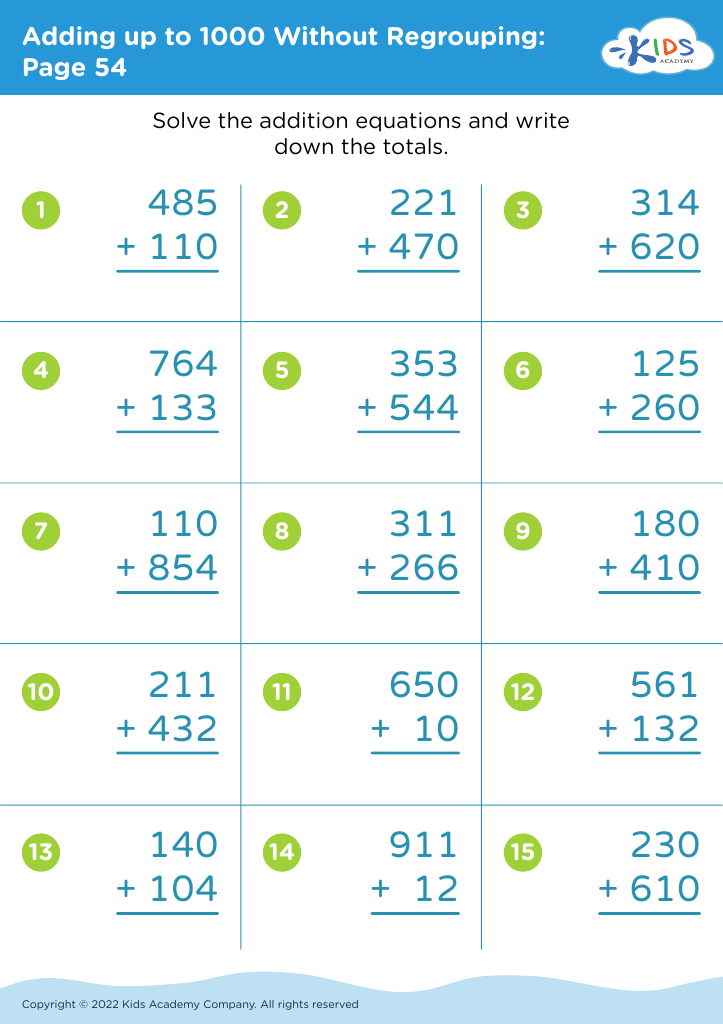

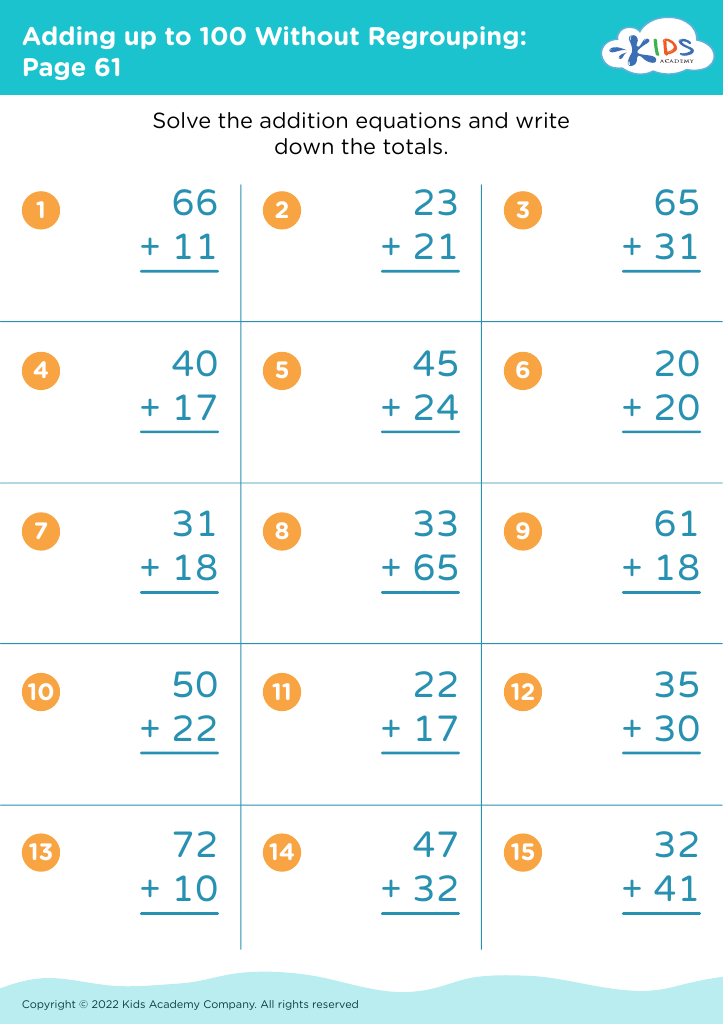
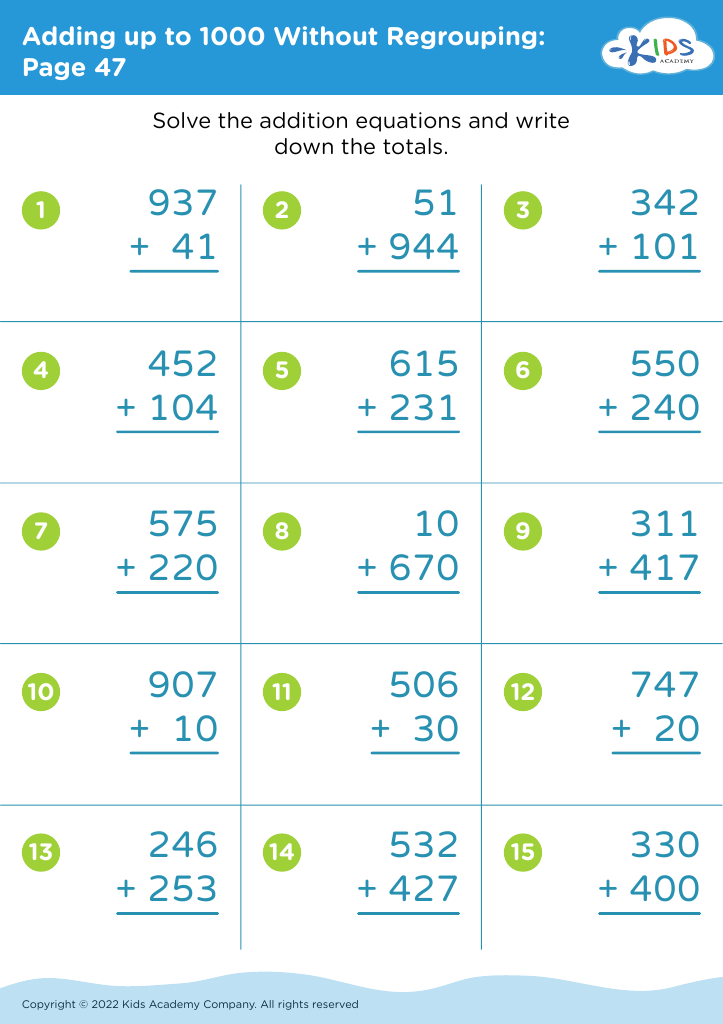
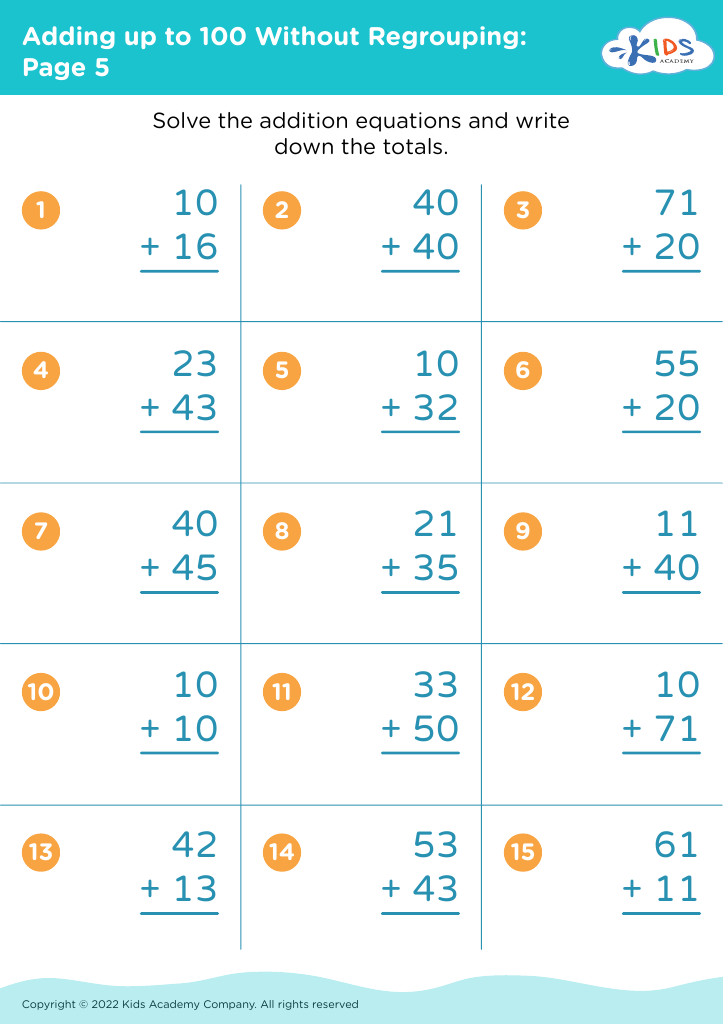





.jpg)













