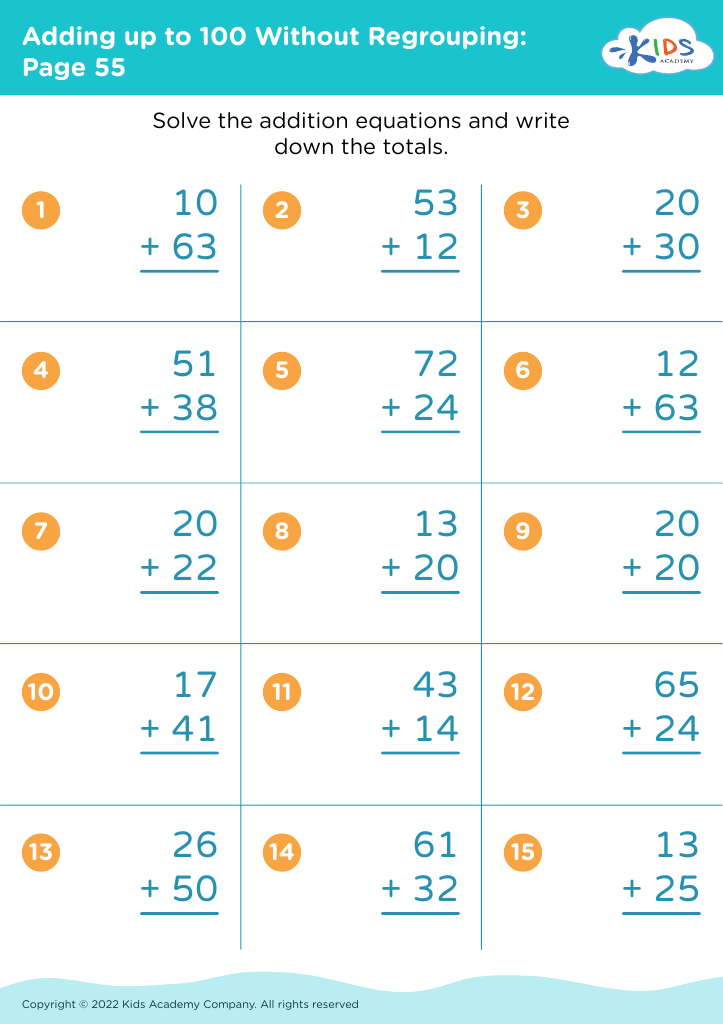
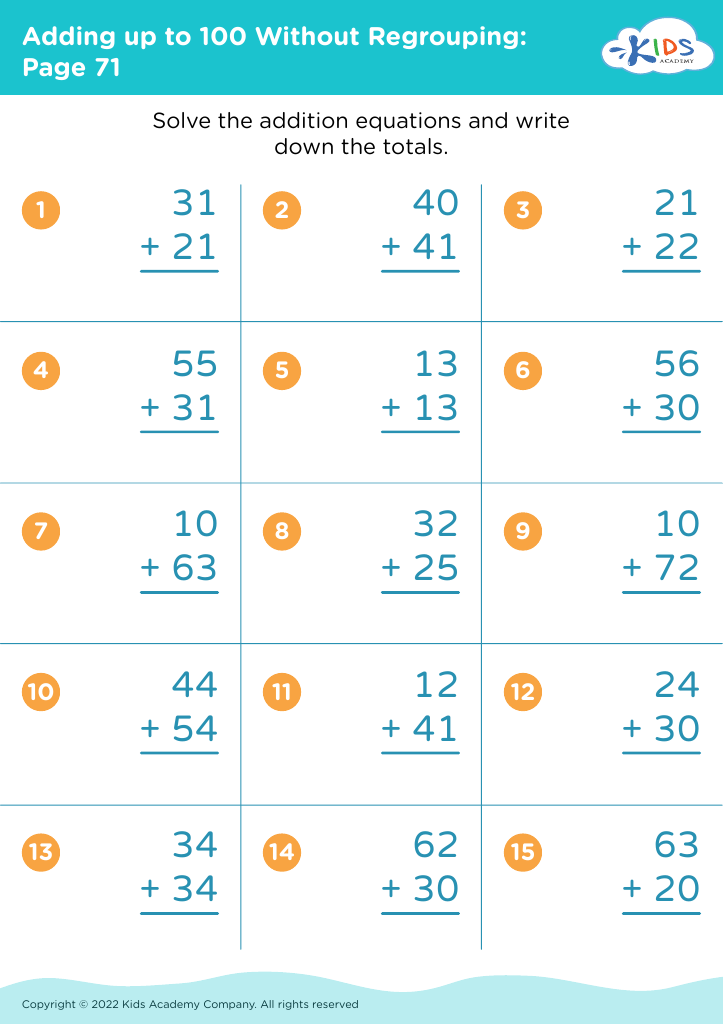
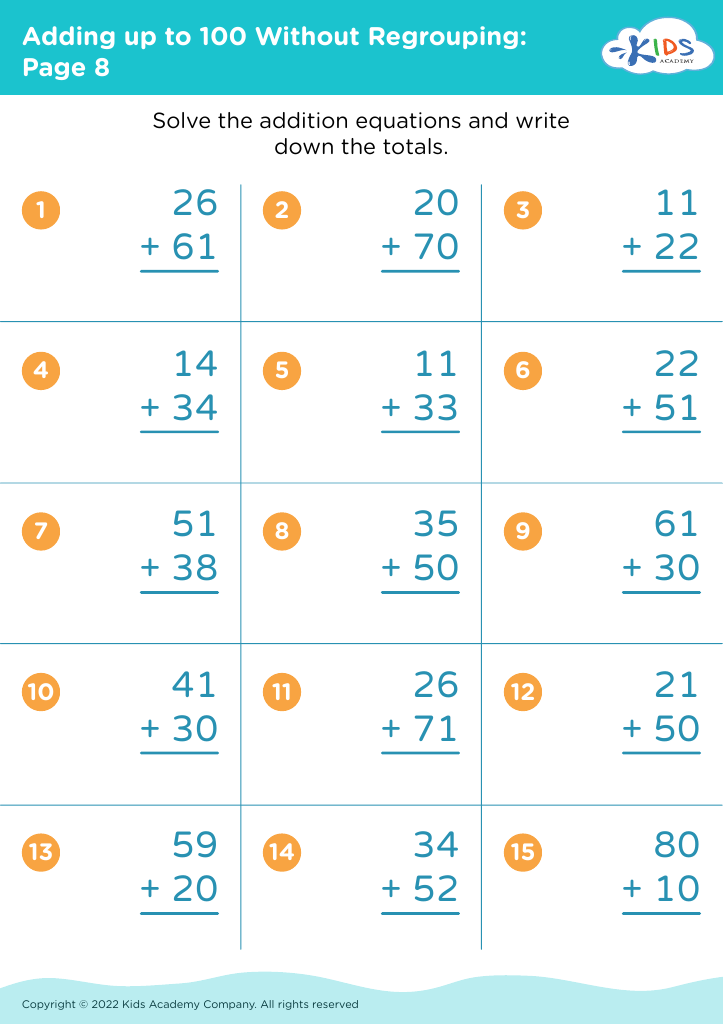
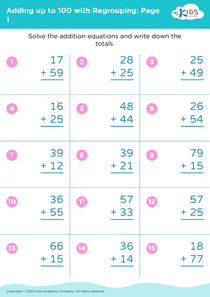
Reading comprehension Adding up to 100 Without Regrouping Worksheets for 7-Year-Olds
3 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's reading comprehension and math skills with our "Reading Comprehension: Adding up to 100 Without Regrouping Worksheets for 7-Year-Olds." These engaging worksheets combine fun stories with arithmetic practice, helping children build better understanding. Each activity features simple addition problems designed to improve accuracy and confidence, along with reading passages that strengthen literacy. Perfect for classroom settings or home practice, these worksheets provide a balanced approach to learning, fostering both mathematical and reading proficiency. Tailored for young learners, they make mastering new skills enjoyable and effective. Explore our collection today and support your child’s educational journey!
Reading comprehension and basic arithmetic skills like adding up to 100 without regrouping are foundational elements that significantly impact a child's overall academic and developmental growth. For 7-year-olds, these skills are intertwined in fostering critical cognitive abilities important for later learning.
Firstly, reading comprehension allows children to understand and interpret written information, a crucial skill for all subjects, not just language arts. Young readers who comprehend what they read can better follow instructions, process information, and engage with learning materials independently. This autonomy builds confidence and motivation, encouraging a positive attitude toward lifelong learning.
Secondly, mastering arithmetic skills, such as adding up to 100 without regrouping, develops numerical literacy and logical reasoning. Arithmetic exercises improve memory, attention to detail, and problem-solving skills. These skills form the foundation for more complex mathematical concepts and applications that students will encounter in their educational journey.
Integrating these skills in a holistic manner—like understanding word problems that require addition—enhances a child's ability to apply both literacy and math skills practically. This integrated approach nurtures well-rounded learners who can think critically and approach various problems successfully. Hence, paying attention to both reading comprehension and arithmetic is essential for laying a robust educational foundation for 7-year-olds, ensuring their success in future academic endeavors.