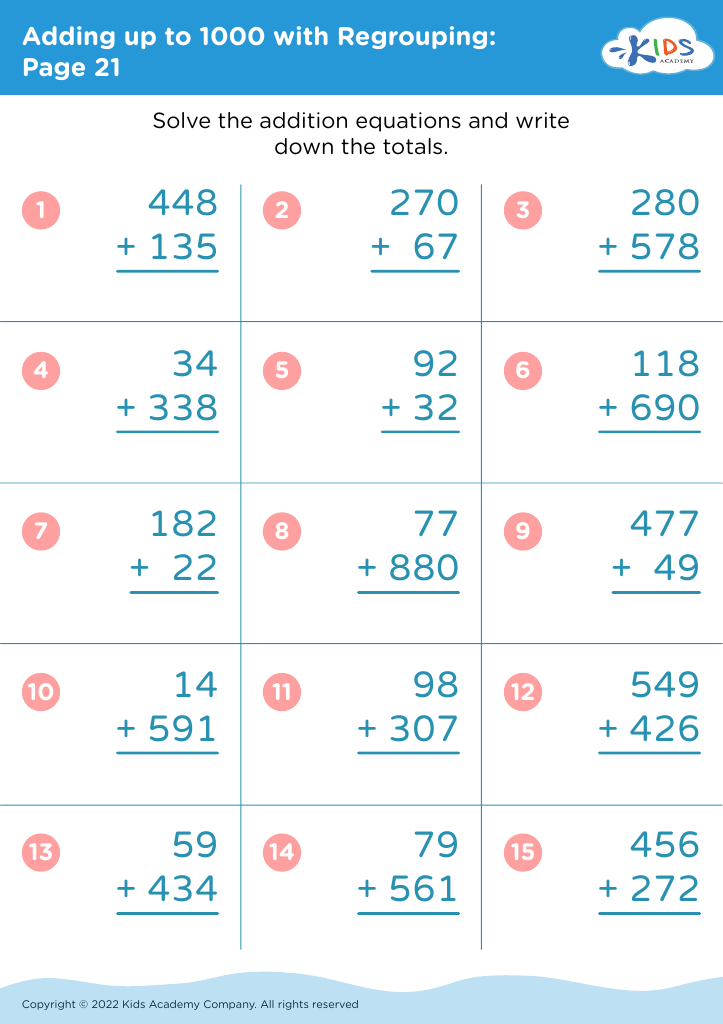
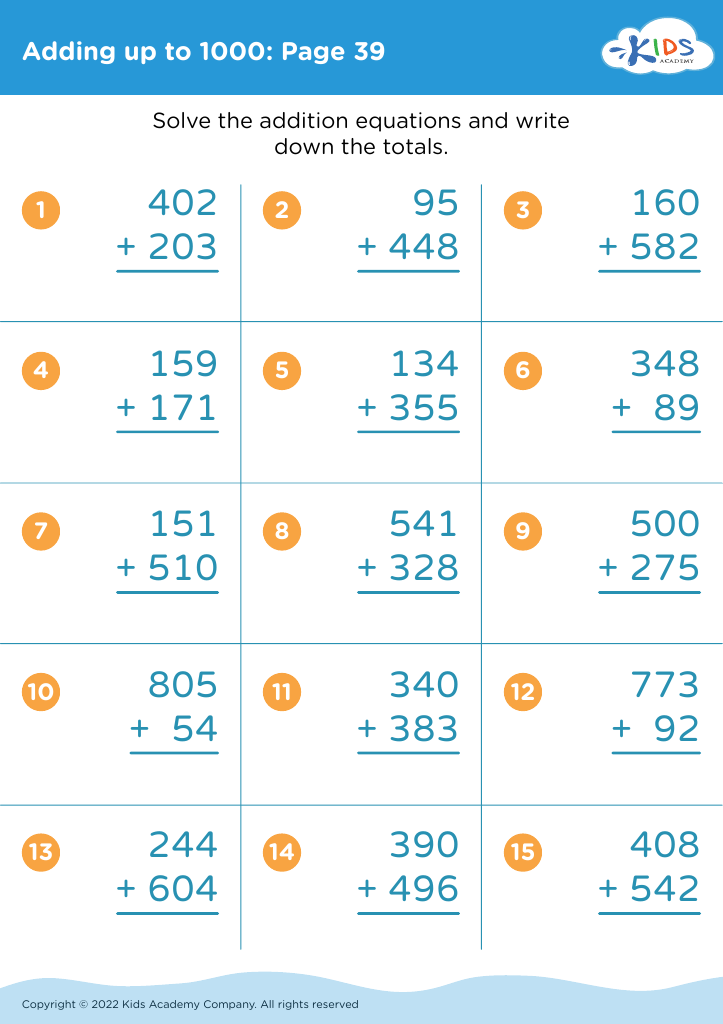
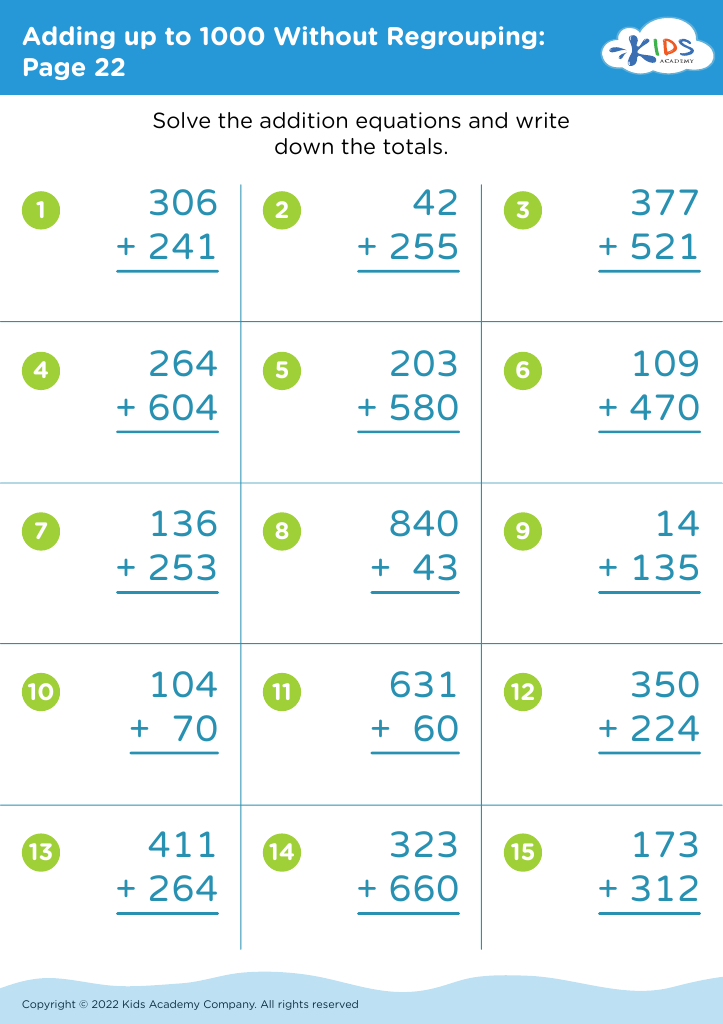
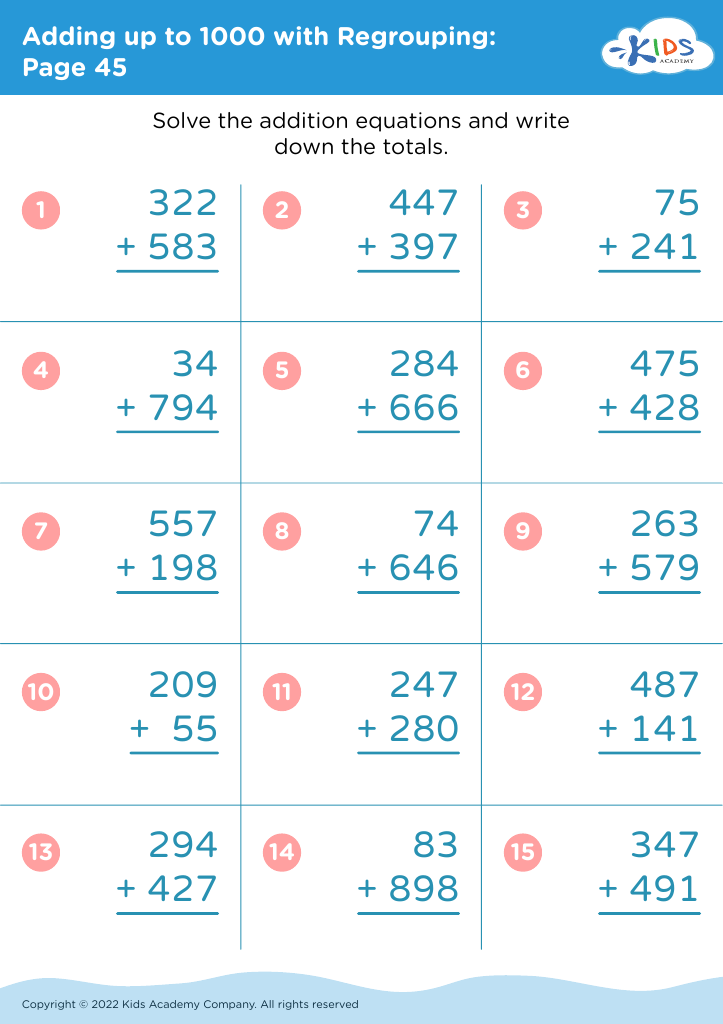
Fine motor skills (writing) Adding up to 1000 Worksheets for Ages 8-9
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's fine motor skills and writing abilities with our comprehensive collection of "Adding up to 1000" worksheets designed for ages 8-9. These engaging activities not only promote numerical proficiency but also focus on developing essential writing skills by encouraging children to practice handwriting while they work on math problems. Our worksheets feature a variety of exercise formats to keep your child motivated and challenged. Each printable resource is crafted to provide an enjoyable learning experience, ensuring that your child gains confidence and improves their coordination. Discover the perfect balance of fun and education today with our fine motor skills writing worksheets!
Fine motor skills are crucial for children aged 8-9, significantly influencing their writing development, academic performance, and overall confidence. During this stage, children are refining their ability to manipulate small objects, which directly impacts their handwriting clarity, precision, and fluency. Effective writing is vital for expressing thoughts, completing assignments, and participating in assessments.
Parents and teachers should prioritize fine motor skills because they correlate strongly with a child's academic success. Children with strong fine motor abilities can write faster and with greater accuracy, allowing for a smoother, more engaging learning experience. Conversely, those who struggle may become frustrated, exhibiting a lack of motivation and self-esteem in academic settings.
Moreover, fine motor skills extend beyond writing; they are foundational for numerous everyday tasks—everything from tying shoelaces to using scissors. Encouraging activities that boost these skills—like crafting, playing with building blocks, or engaging in puzzles—can foster a sense of accomplishment and joy in learning.
In conclusion, nurturing fine motor skills at this age equips children with essential tools for writing and broader life skills, promoting their academic journey and preparing them for future challenges. Parents and teachers play a vital role in facilitating this crucial aspect of development.