Understanding money Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 8-9
4 filtered results
-
From - To
Our "Understanding Money: Addition & Subtraction Worksheets for Ages 8-9" are expertly designed to build essential math skills while engaging young students. These worksheets use real-world scenarios to teach children how to add and subtract amounts of money, helping them develop a strong grasp of basic math operations within the context of everyday transactions. Perfect for reinforcing classroom learning, each sheet presents practical problems that encourage critical thinking and problem-solving. Ideal for both home and school use, our worksheets make learning about money fun and educational, ensuring kids gain confidence in handling money and calculations.
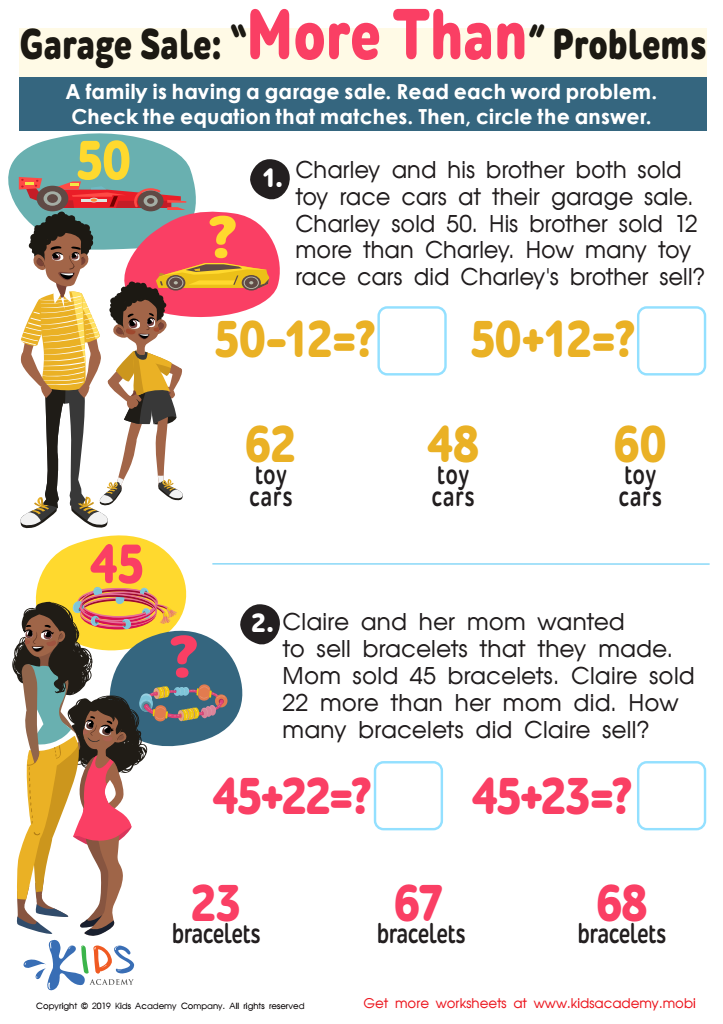

Garage Sale - More yhan Worksheet
Understanding money, including the essentials of addition and subtraction, at the ages of 8-9 is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it lays the foundation for practical life skills. Grasping how to add and subtract money helps children understand the value of currency, preparing them for real-world scenarios like shopping or managing their allowance. This practical application makes mathematical concepts more relatable and enjoyable, fostering a positive attitude toward learning math.
Secondly, understanding money promotes cognitive development. It enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills. For instance, when children figure out how much change they should get or calculate the total cost of multiple items, they engage in logical reasoning and mental math, which bolsters their overall mathematical proficiency.
Thirdly, instilling these skills early can build financial literacy, an essential competency in today's economy. From budgeting to saving, early exposure helps cultivate responsible financial habits. When parents and teachers emphasize the importance of managing money through basic additions and subtractions, they equip children with the knowledge needed for future financial decisions.
Lastly, a good grasp of money concepts boosts confidence. Children who can handle money accurately feel more independent and self-assured. This early confidence can translate to academic success and a proclivity for tackling more complex concepts as they grow older.
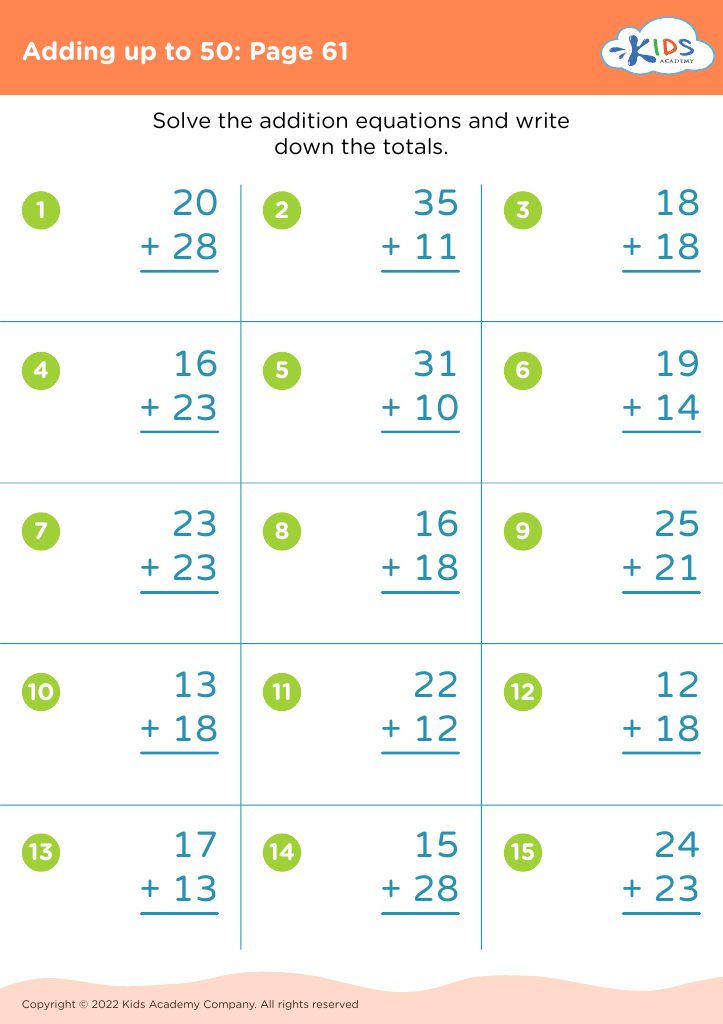

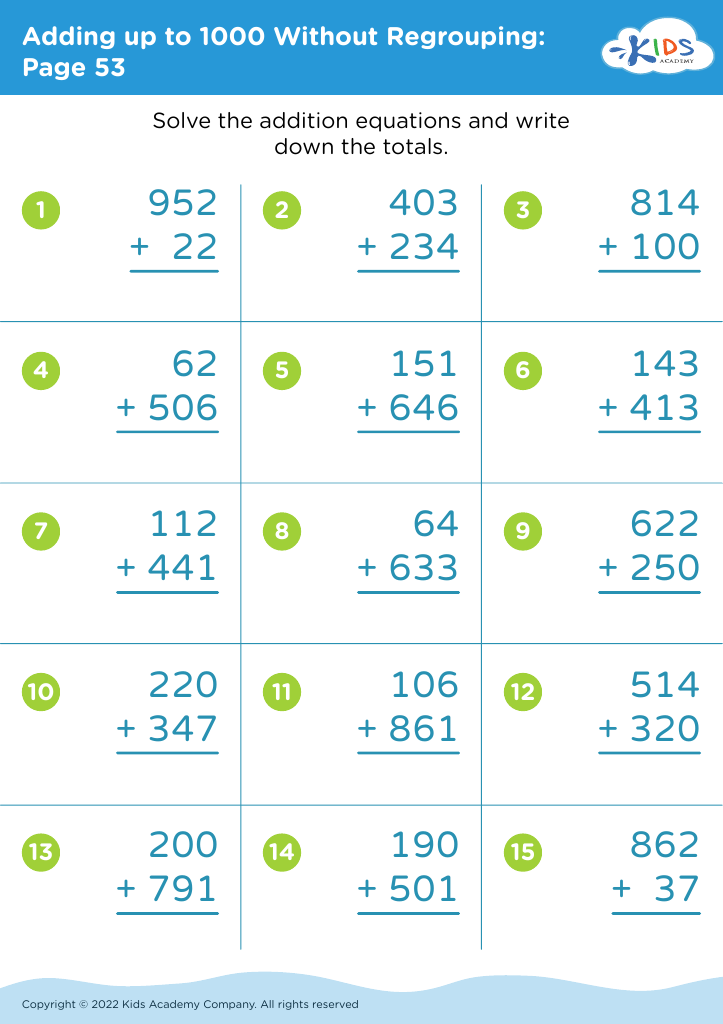
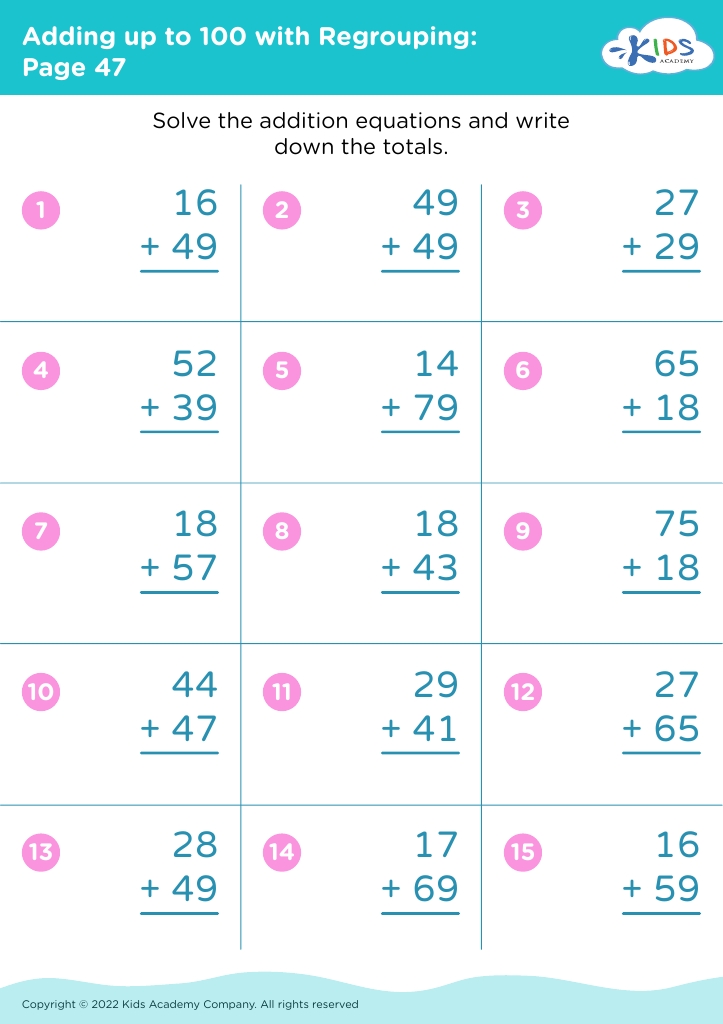
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students



















