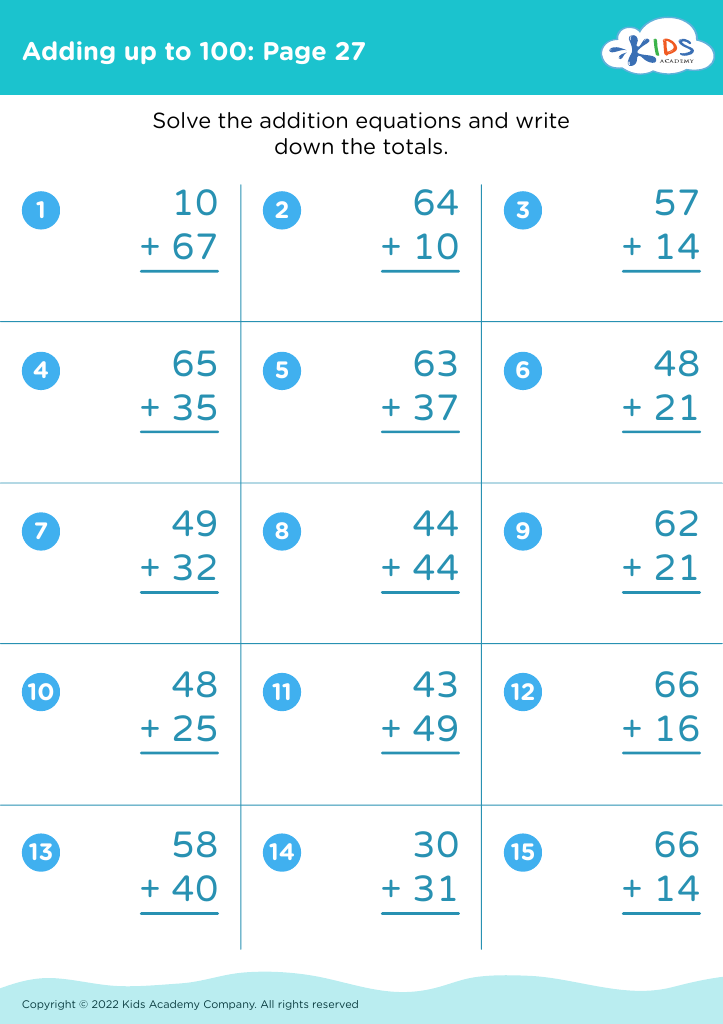
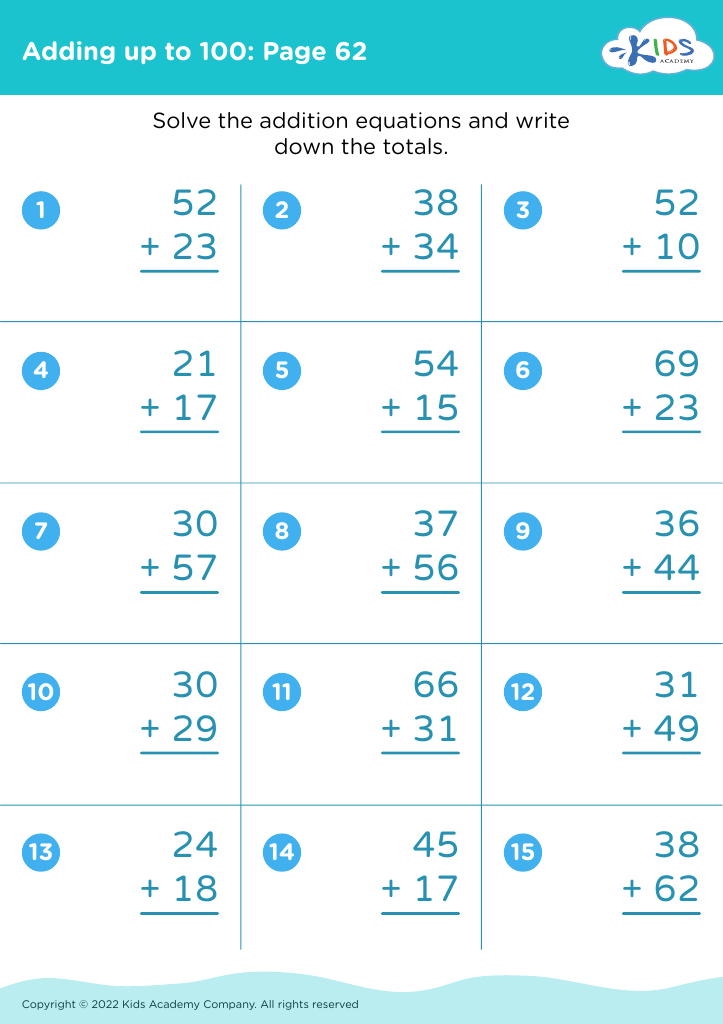
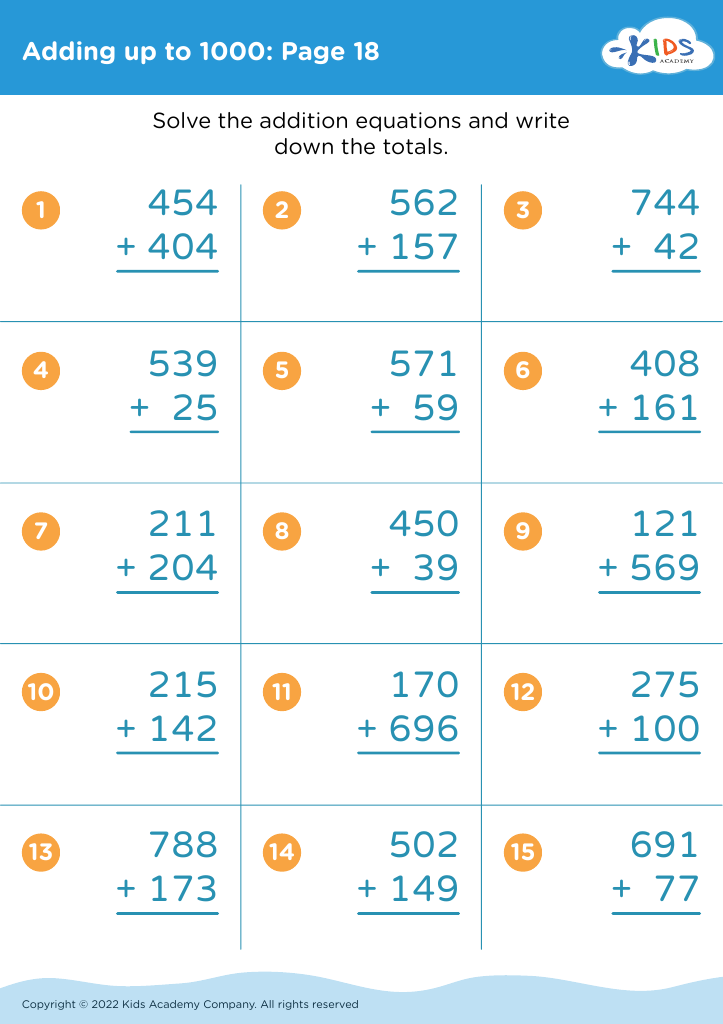
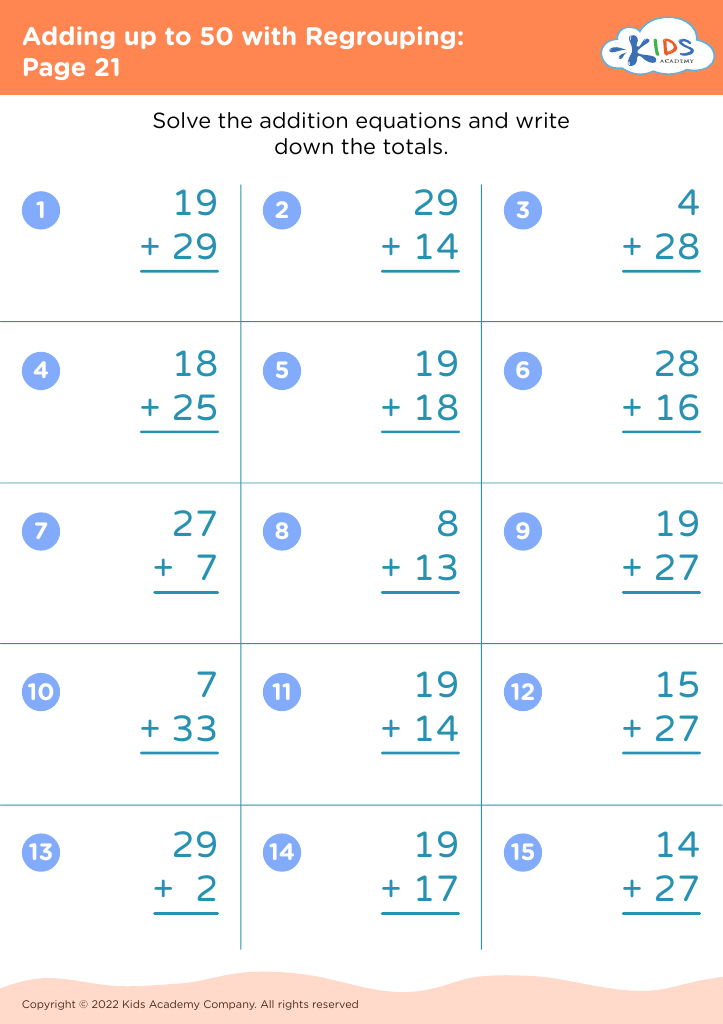
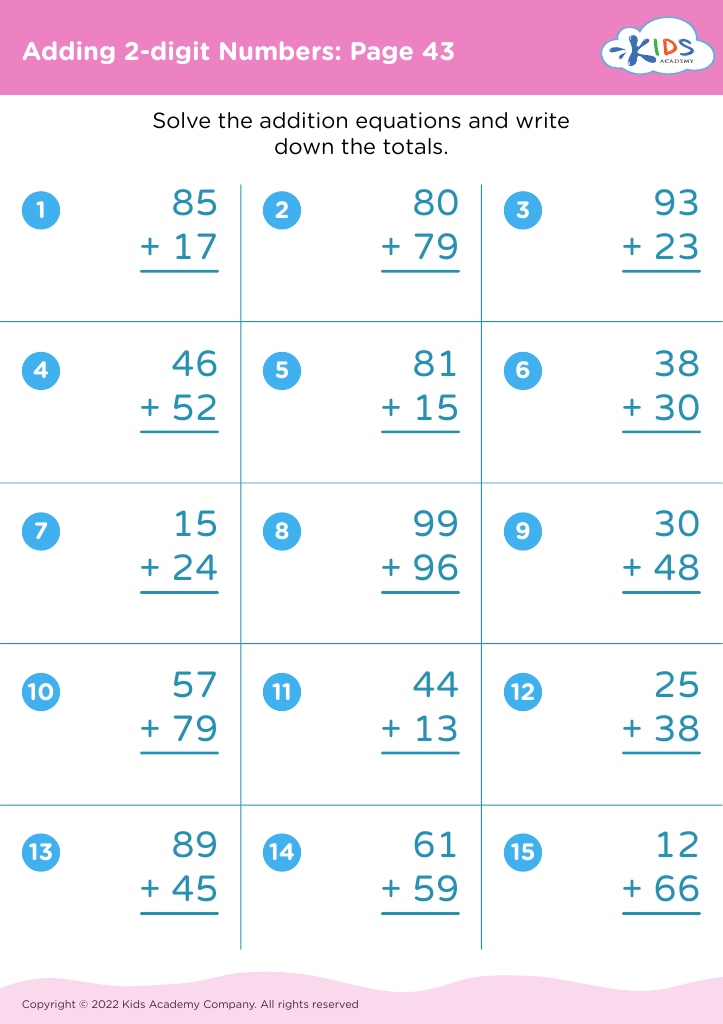
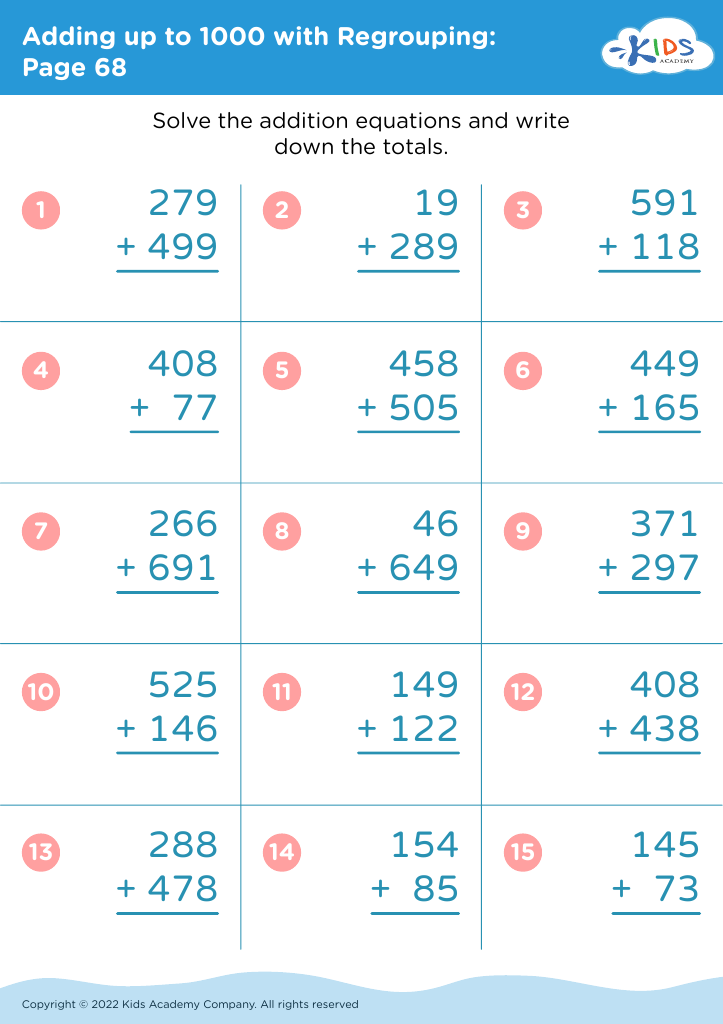
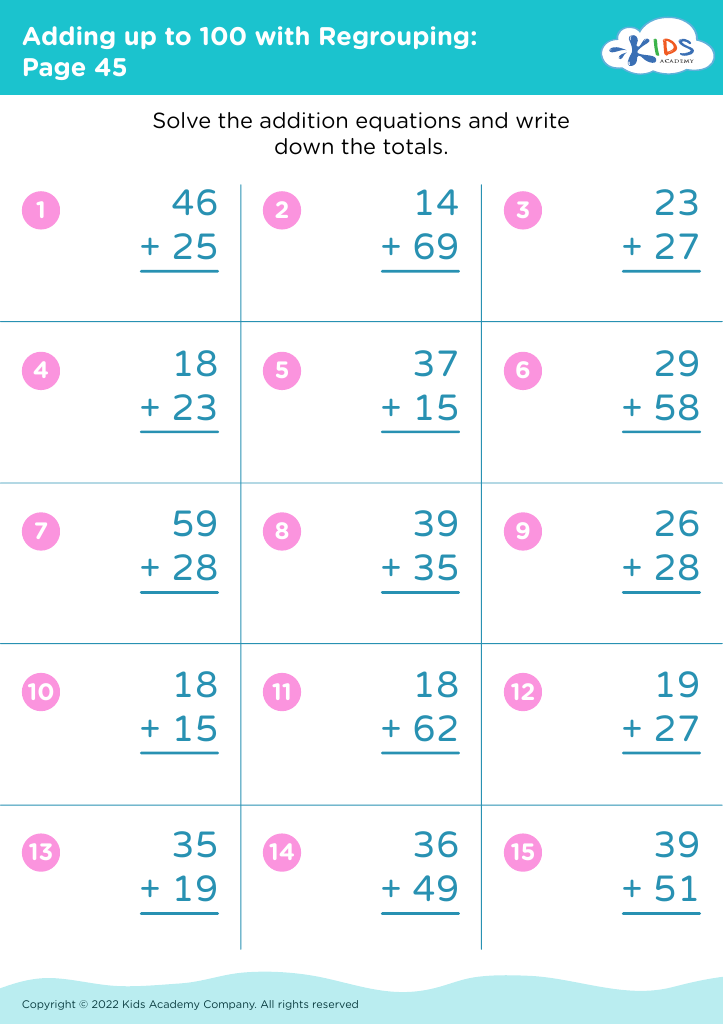
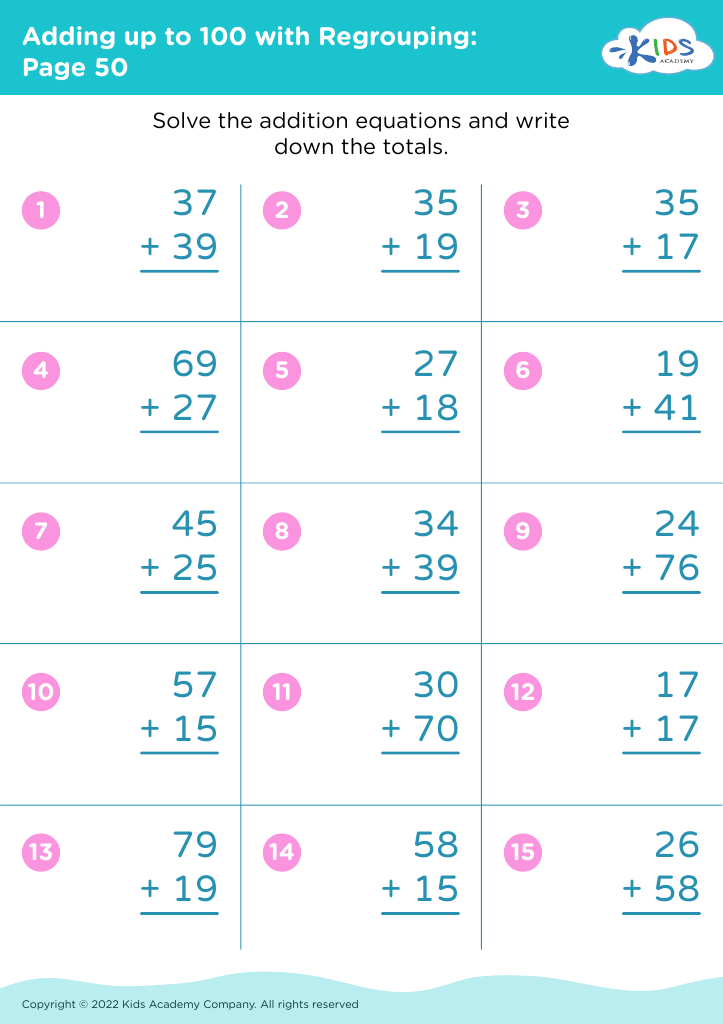
Fine Motor Skills Addition Worksheets for 8-Year-Olds - Page 2
35 filtered results
-
From - To
Fine motor skills are crucial for 8-year-olds as they directly impact a child's ability to perform daily tasks, engage in academic activities, and develop independence. These skills involve the use of small muscles for tasks like writing, using scissors, and manipulating small objects, which are foundational as children progress through school.
Parents and teachers should prioritize the development of these skills because strong fine motor abilities enhance handwriting, improve hand-eye coordination, and foster problem-solving skills. When children manipulate objects, they build hand strength and dexterity, which can boost their confidence and encourage a positive attitude toward learning. Moreover, maintaining fine motor skills can help prevent frustration regarding tasks that require precision, such as drawing or completing puzzles.
Supporting fine motor development involves providing children with engaging activities like arts and crafts, building with blocks, or playing with modeling clay. These playful yet purposeful practices lay the groundwork for future academic success, impacting skills across subjects like math and science, where precision is essential. By focusing on fine motor skills, parents and teachers can ensure children are well-equipped for the challenges of schooling and everyday living, setting the stage for a lifetime of learning and self-sufficiency.