Fine Motor Skills Extra Challenge Worksheets for Ages 4-9 - Page 2
47 filtered results
-
From - To
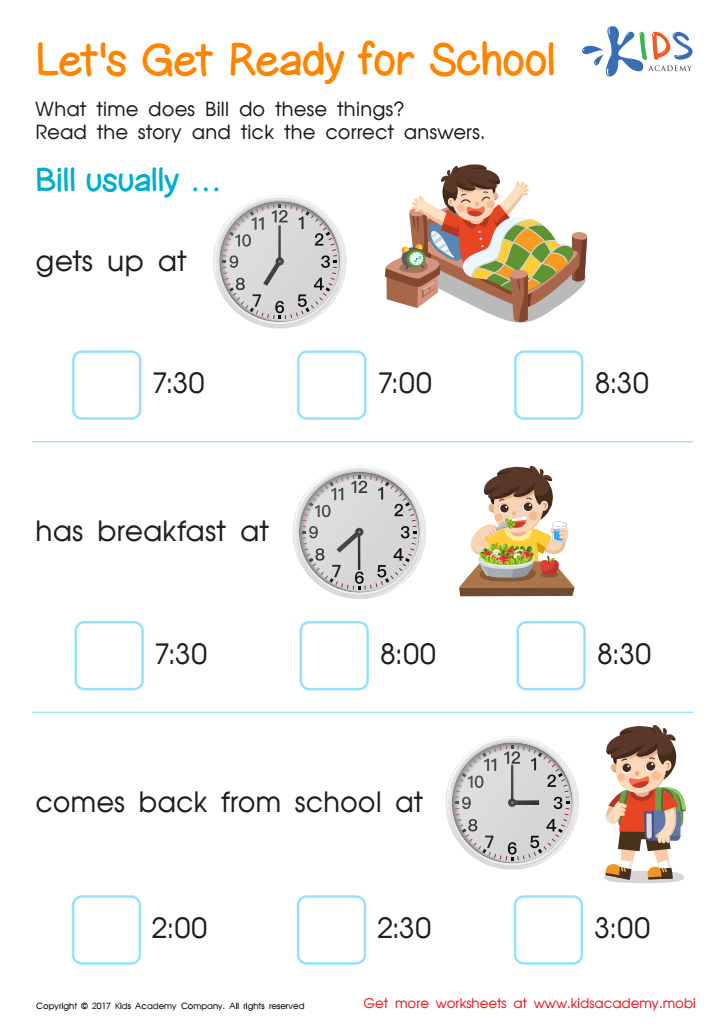

Lets Get Ready For School Time Printable


Woodpecker and Triangles Worksheet
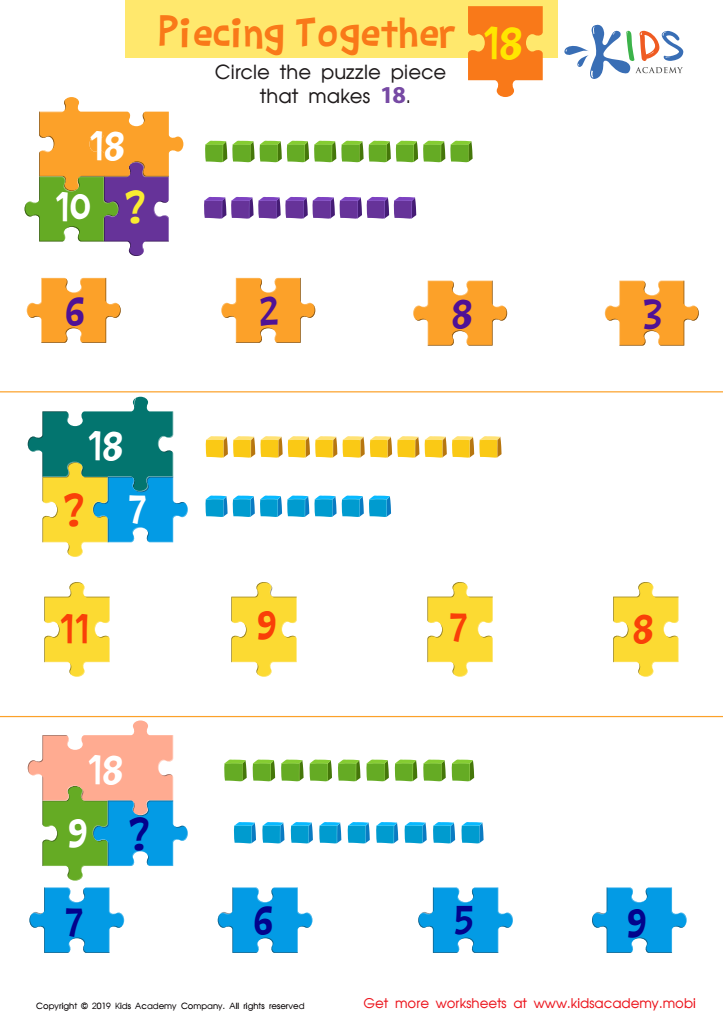

Piecing Together 18 Worksheet
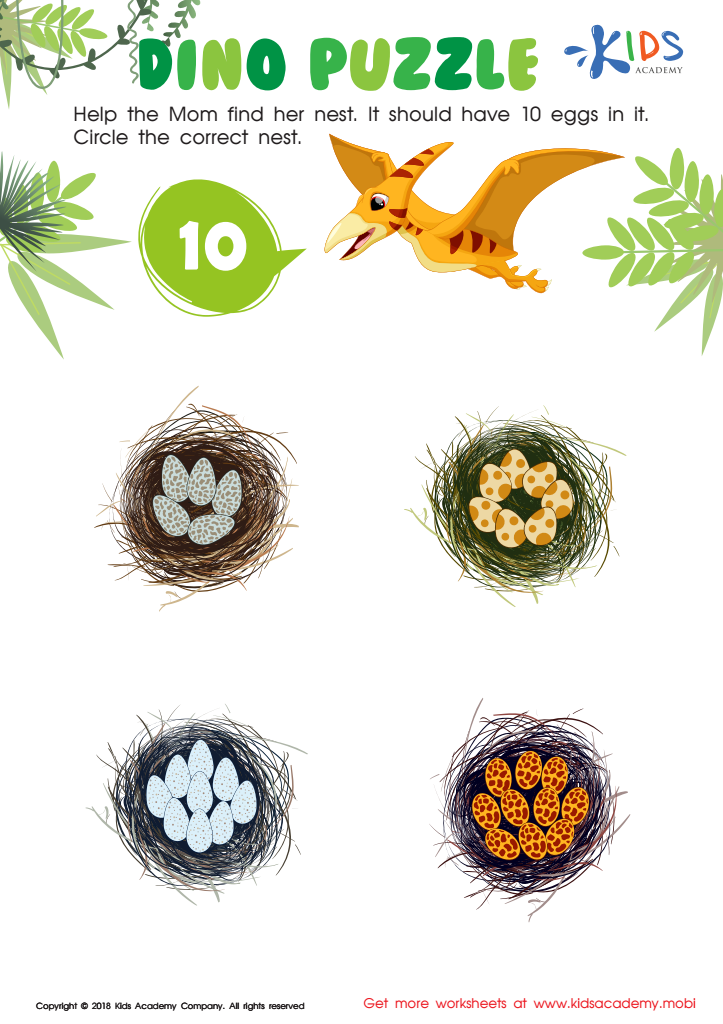


Learn Number For Kindergarten Worksheet
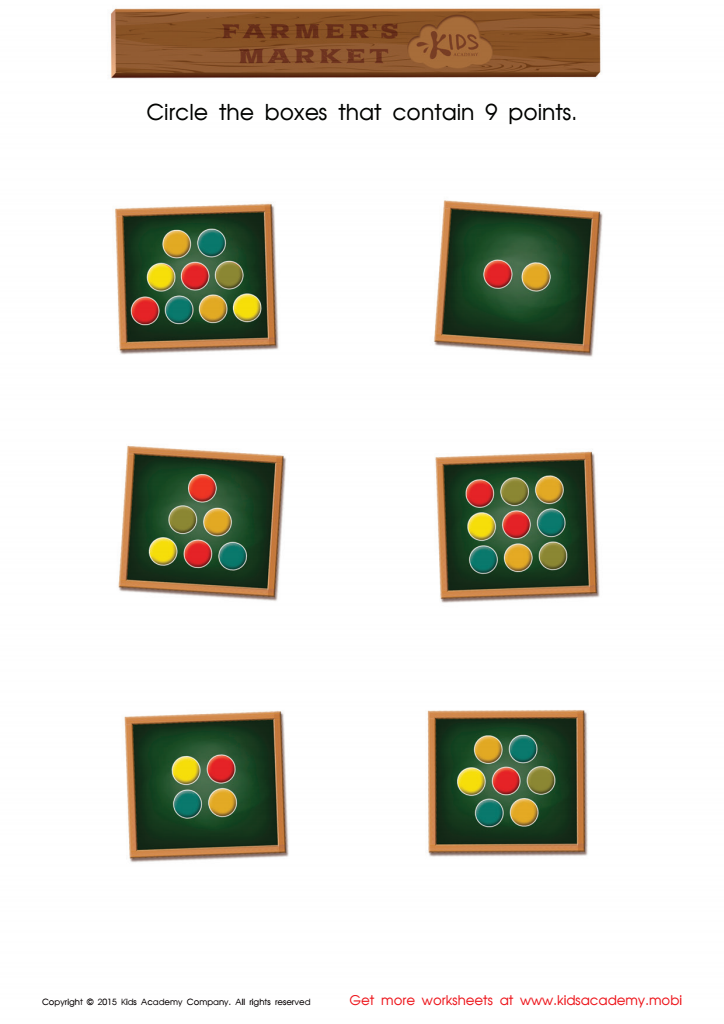

Count and Match Points 9 Math Worksheet


Honey Bee Counting Worksheet


Count Santa's Presents Worksheet
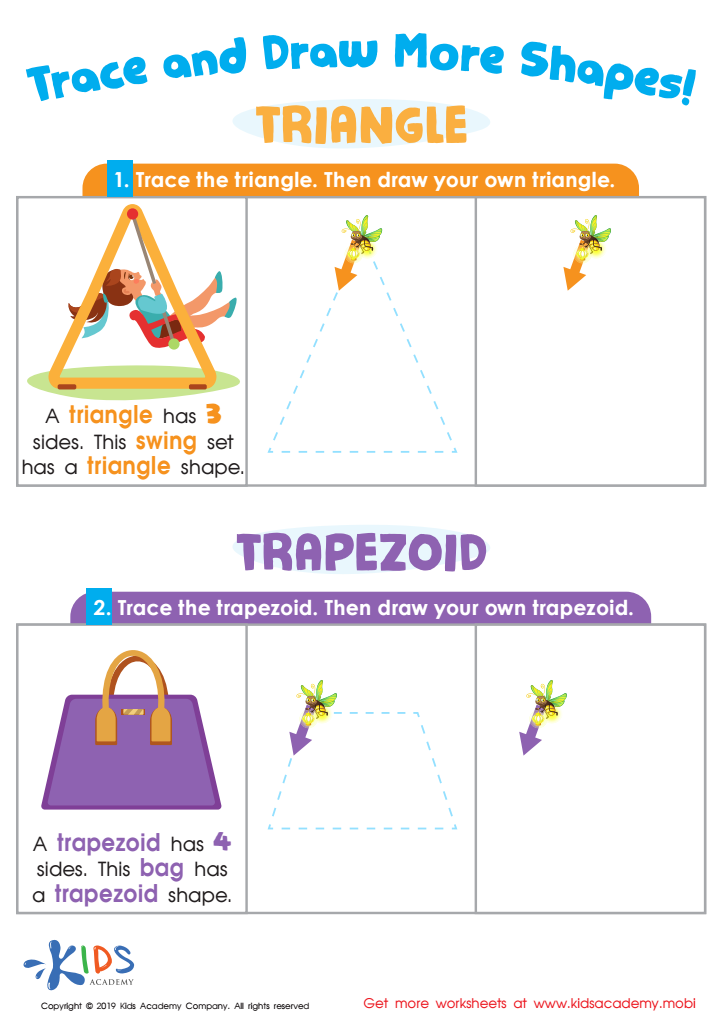

Trace and Draw More Shapes Worksheet


Letter V Tracing Page


Counting Butterflies Worksheet


The Circle Maze Worksheet


Santa Claus Tracing Winter Words Worksheet


Pirate Ship Connect Dots Worksheet
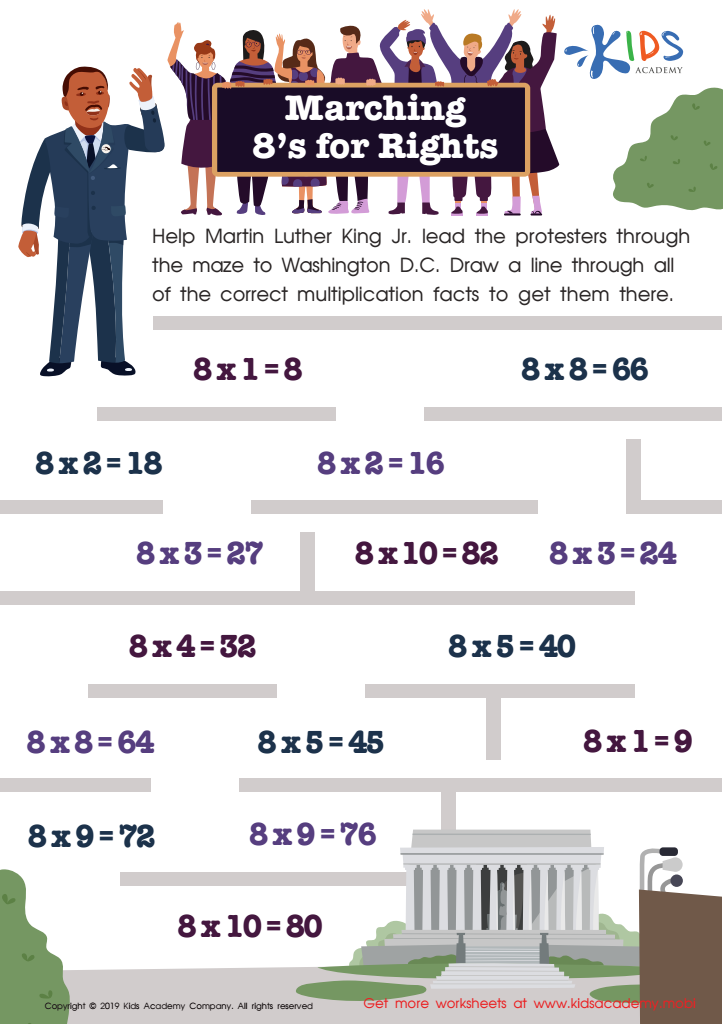

Marching 8’s for Rights Worksheet


Pilgrim Maze Worksheet


Find Words Mouse Maze Worksheet


Three Little Piggies Printable Coloring Page


Princess Connect Dots Worksheet

Letter T Tracing Page

Big Bad Wolf Printable Coloring Page




Count and Match: Feed the Animals Worksheet
Fine motor skills refer to the coordination between small muscles, specifically in the hands and fingers, that allow for precise movements. For children aged 4-9, developing these skills is crucial as it directly impacts their ability to perform everyday tasks efficiently. Parents and teachers should care about fine motor skills' cultivation because it fosters independence and autonomy in children when managing daily activities such as buttoning clothes, tying shoelaces, using utensils, and brushing teeth.
In an academic setting, well-developed fine motor skills are integral to writing, drawing, cutting, and manipulating small objects, which are foundational for school readiness and success. Writing, in particular, requires a good grip and controlled hand movements, ensuring legibility and endurance during longer tasks.
Fine motor skill challenges also impact cognitive development. Engaging with activities that promote these skills enhances children's problem-solving abilities, hand-eye coordination, and spatial awareness. Additionally, tasks requiring fine motor skills often come with an intrinsic educational element, like counting beads or shaping letters, further solidifying academic concepts.
Lastly, fine motor activities can also stimulate creativity and boost confidence, as children feel proud when they can accomplish tasks on their own. Early intervention by parents and teachers can thus provide support where necessary, ensuring children do not lag in these crucial developmental areas.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students