Hand-eye Coordination Normal Phonics Worksheets for Ages 3-6
5 filtered results
-
From - To
Enhance your child's hand-eye coordination while developing essential phonics skills with our engaging Normal Phonics Worksheets, specifically designed for ages 3-6. These worksheets incorporate fun activities that help reinforce letter recognition, sound association, and pre-reading abilities, all while promoting motor skills through tracing and coloring exercises. By blending entertaining tasks with educational content, your little ones will enjoy learning in a stimulating, enjoyable environment. Perfect for parents and educators, these resources cater to diverse learning styles and encourage interactive play. Start your child's phonics journey today and build a strong foundation for their literacy development!
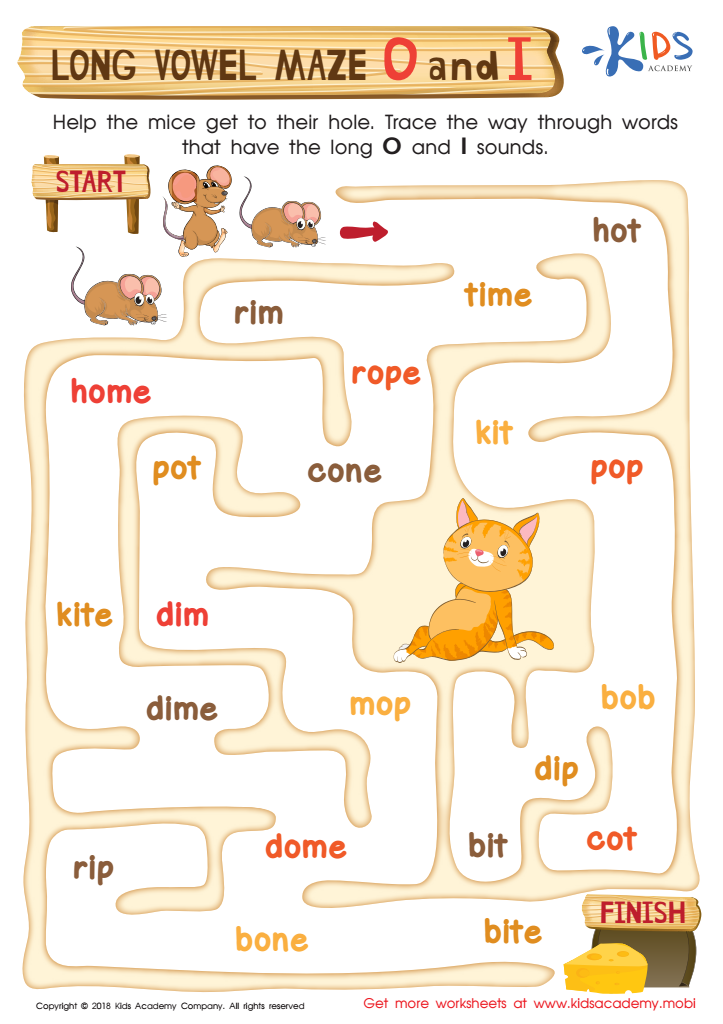

Long Vowel Maze /o/ and /i/ Worksheet
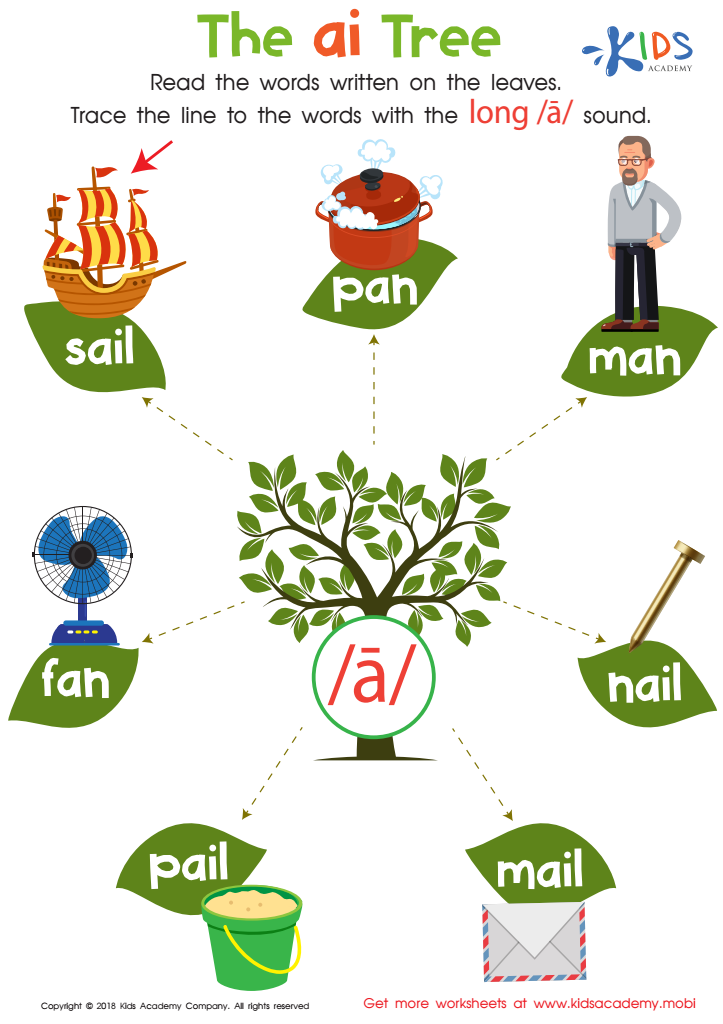

The AI Tree Worksheet
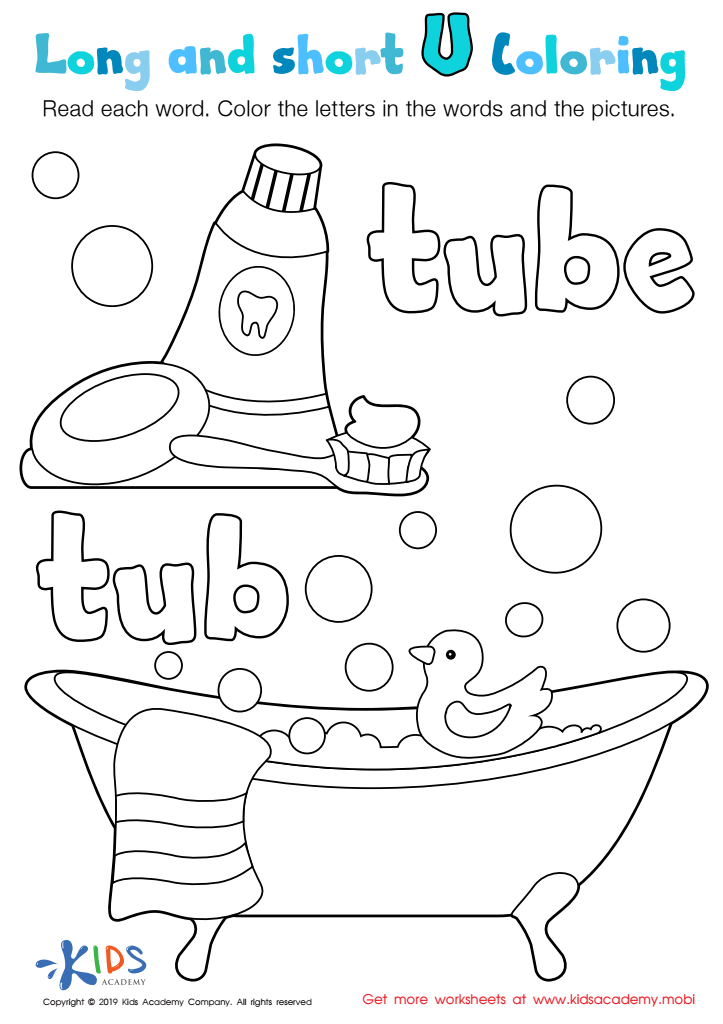

Long and Short U Worksheet


Feed the Whale Worksheet


Long and Short E Worksheet
Hand-eye coordination is a crucial skill for young children, particularly between the ages of 3 to 6, as it directly impacts their ability to learn and engage with their environment. Parents and teachers should care about developing hand-eye coordination through Normal Phonics activities because this skill is intertwined with literacy and overall development.
Normal Phonics incorporates visual and auditory elements while requiring children to use their hands to interact with letters, sounds, and words. For example, activities like tracing letters or matching letters and objects can significantly improve their coordination. Such practices not only enhance fine motor skills but also reinforce cognitive functions necessary for reading and language acquisition.
Furthermore, strong hand-eye coordination aids in a child's ability to focus and follow instructions, essential components of a structured learning environment. As children gain confidence in their motor skills, they are more likely to participate in other classroom activities, promoting social interaction and cooperative learning.
In summary, emphasizing hand-eye coordination through Normal Phonics equips children with vital skills for academic success and personal growth, making it a priority for educators and parents alike in early childhood development.

 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students




















