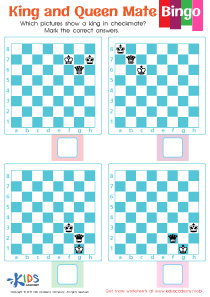
Problem-Solving Skills Normal Chess Worksheets for Ages 3-6
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Introduce your child to the fascinating world of chess while developing critical problem-solving skills with our specially designed Normal Chess Worksheets for Ages 3-6. These engaging activities seamlessly blend play and learning, helping young minds strategize, think ahead, and enhance cognitive abilities. Each worksheet is tailored to be age-appropriate, fostering a love for chess, while subtly promoting logical thinking, patience, and concentration. Ideal for beginners, our vibrant designs captivate interest, and simple exercises ensure that learning is fun and effective. Cultivate a young strategist's mind and watch problem-solving skills flourish through every move. Explore and download now for enriching educational fun!
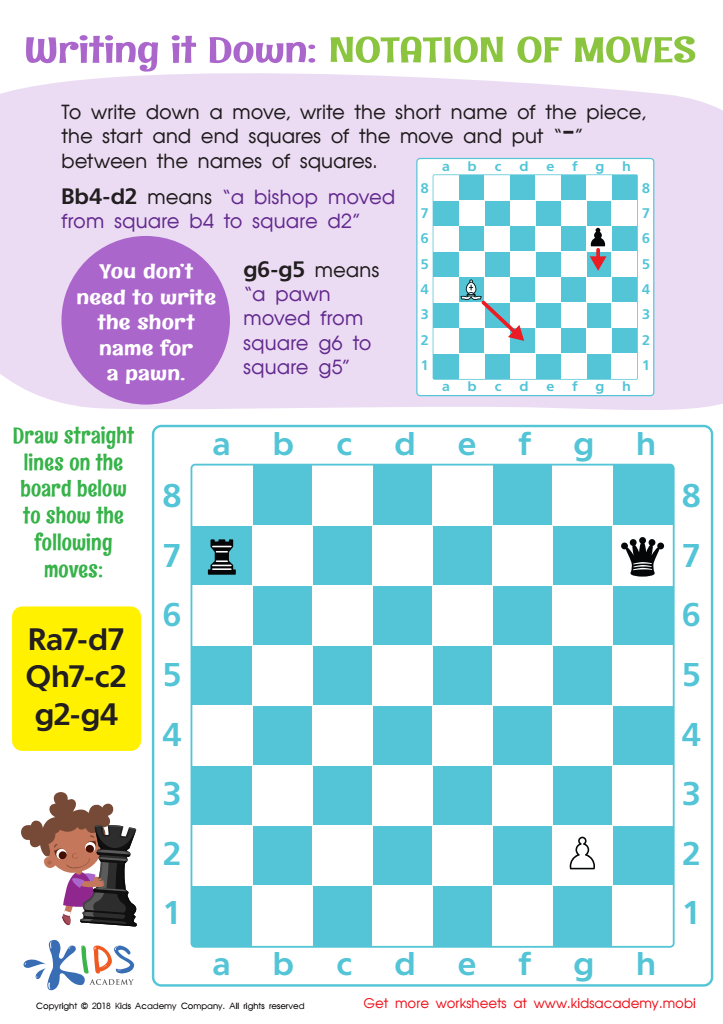

Notation of Moves Writing it Down Worksheet
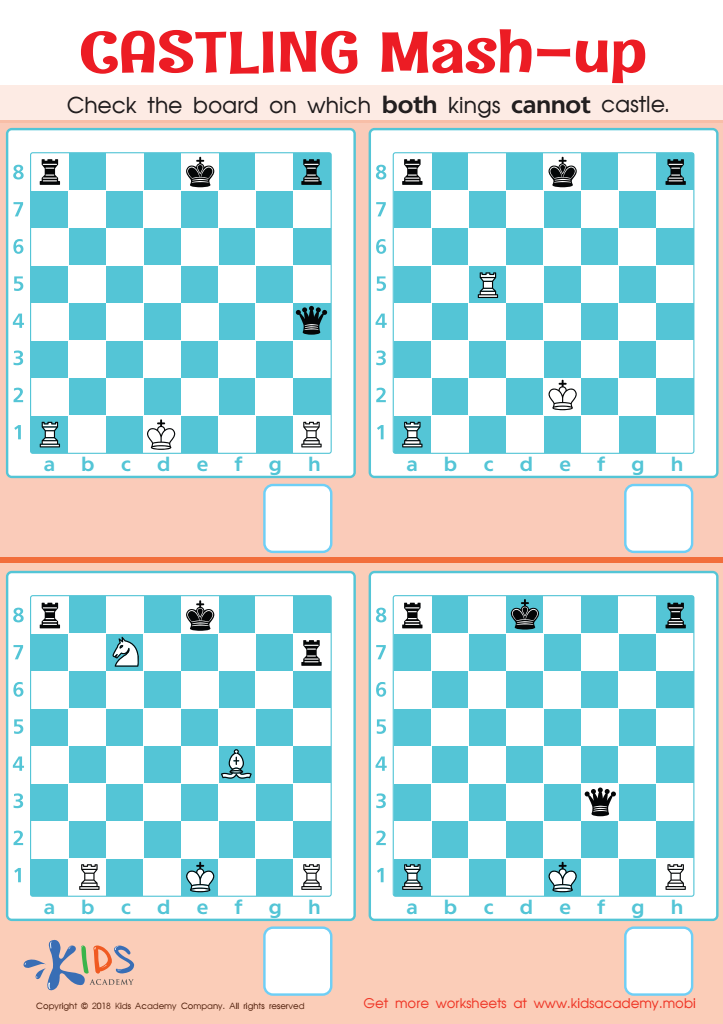

Castling Mash–up Worksheet
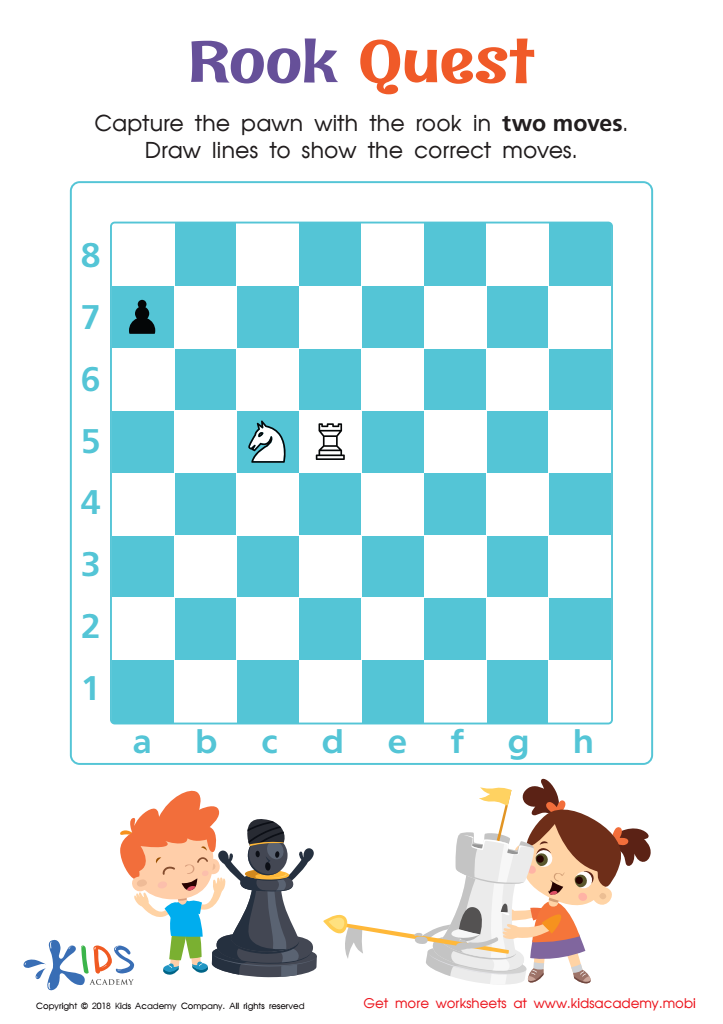

Rook Quest Worksheet
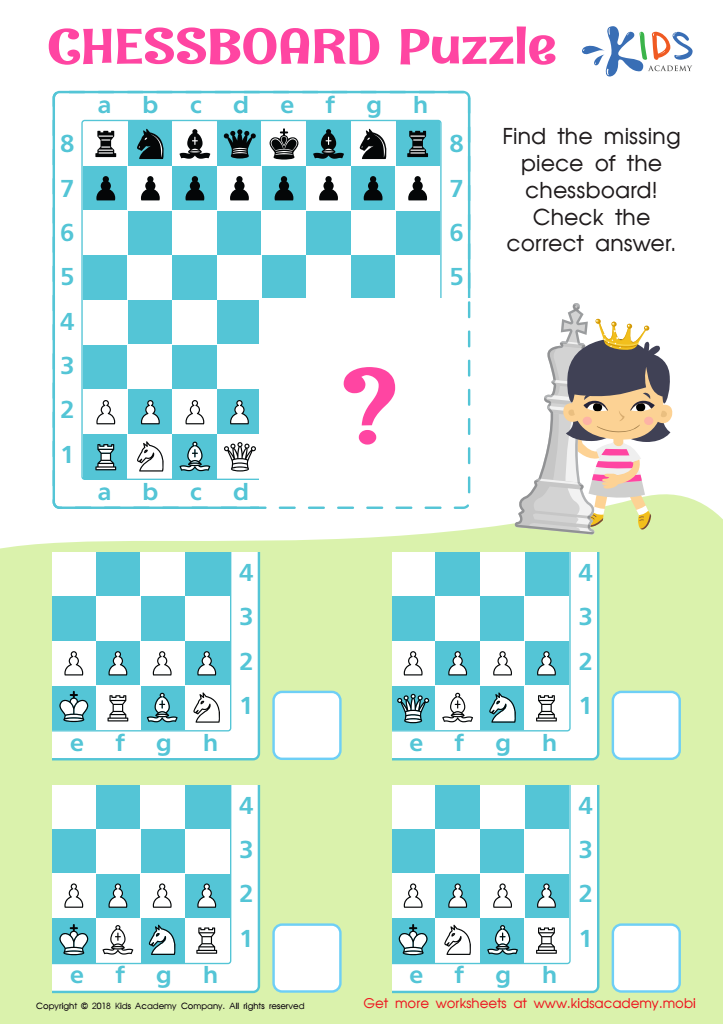

Chessboard Puzzle Worksheet
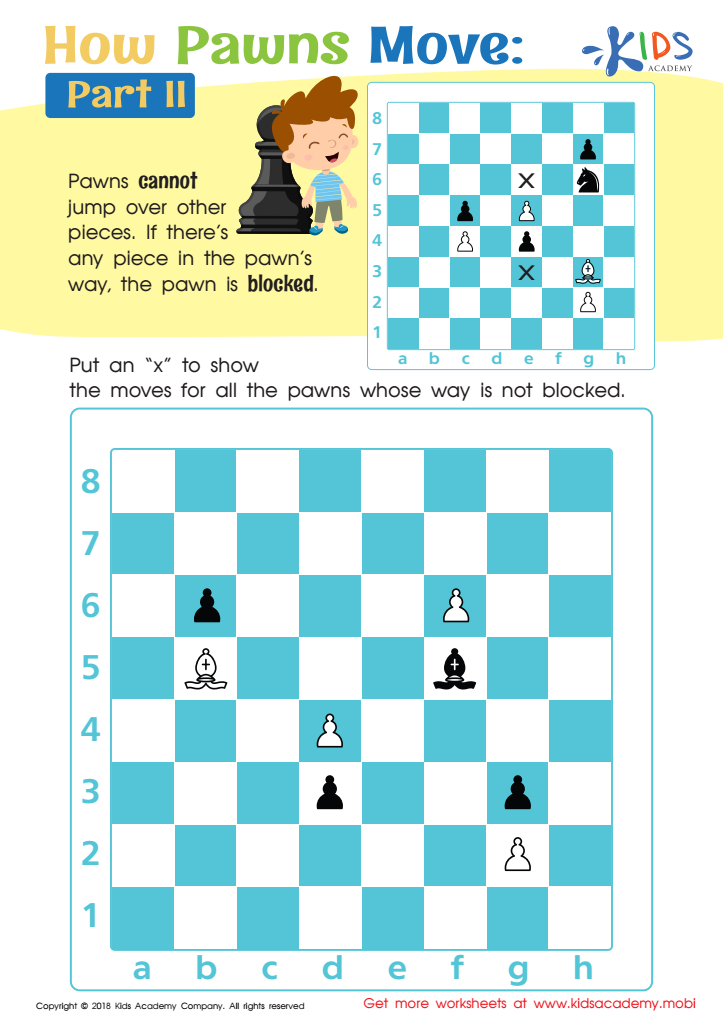

How Pawns Move: Part II Worksheet
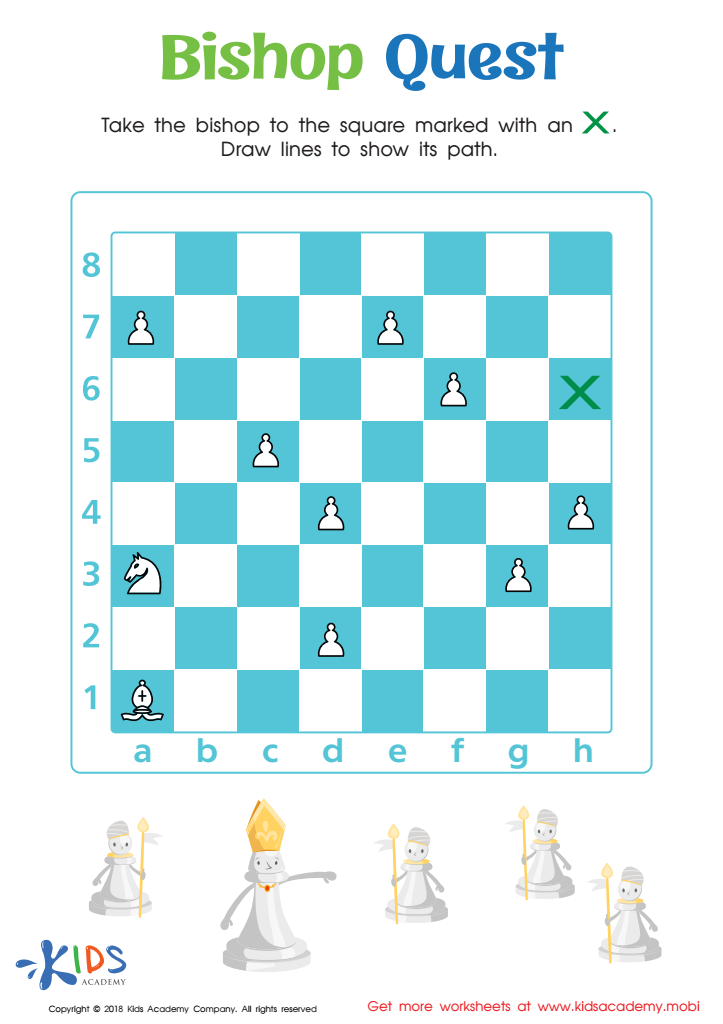

Bishop Quest Worksheet
Problem-solving skills in chess offer significant cognitive and developmental benefits for young children aged 3-6. Parents and teachers should care about these skills because they lay a crucial foundational element in mental development. Engaging in chess encourages critical thinking, patience, and perseverance. When young children are introduced to normal chess, they learn to think ahead and anticipate the consequences of their moves, which cultivates strategic thinking and foresight.
Additionally, chess teaches them the value of planning and decision-making. It promotes logical reasoning by identifying objectives and finding the steps needed to achieve them, thus enhancing their cognitive skills.
Moreover, learning chess from an early age supports attention span and concentration. Each move in the game requires focus and thoughtful consideration, which can translate into better attention and performance in academic areas.
Chess also promotes perseverance, teaching kids to deal with losses and try different approaches to overcome obstacles, fostering resilience. Socially, chess can bridge cultural and language barriers, providing an inclusive environment for collaborative and competitive play.
Therefore, integrating chess into early education can massively benefit a child's intellectual, personal, and social development, providing them with skills that are essential for lifelong learning and success.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students