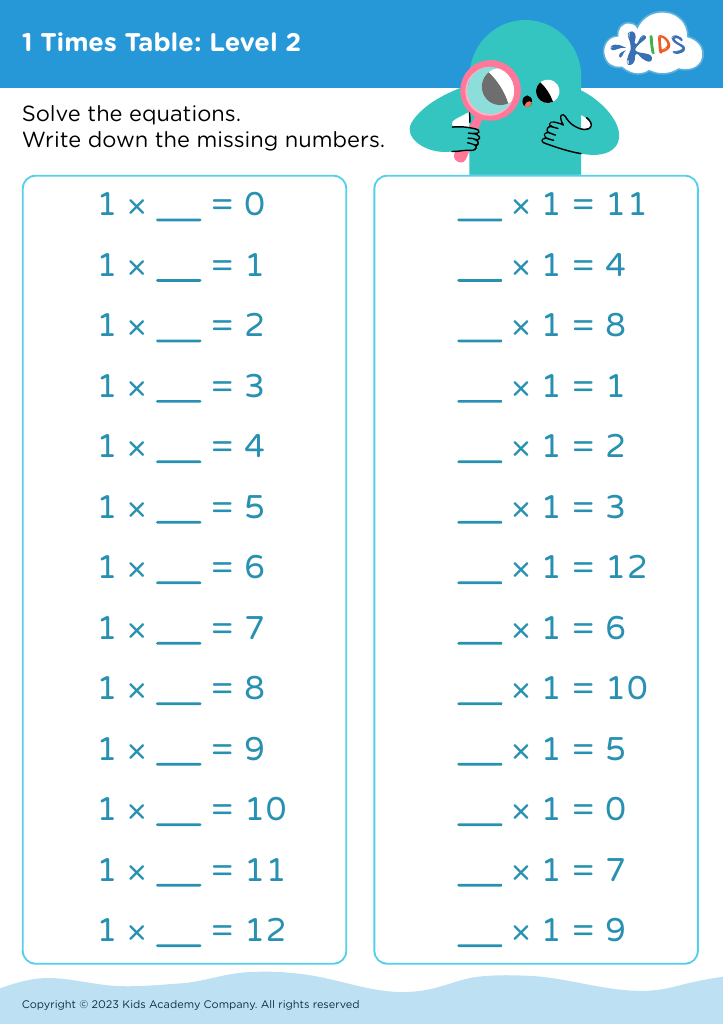
Multiplication practice Normal Multiplication Worksheets for Ages 5-9 - Page 2
26 filtered results
-
From - To
Understanding multiplication forms a crucial foundation for mathematical learning and problem-solving, making it essential for children between the ages of 5-9. During these formative years, children are rapidly developing their cognitive abilities, and introducing multiplication concepts helps enhance their number sense and arithmetic skills.
When parents and teachers invest time in multiplication practice, they provide children with tools for understanding relationships between numbers. It moves beyond simple addition, allowing them to grasp the concepts of grouping and scaling. This understanding is vital not only for immediate math tasks but also for future mathematical topics, including division, fractions, and algebra.
Regular practice aids in memorization and fluency, enabling quicker recall of multiplication facts. This efficiency reduces cognitive load, so children can focus on more complex problem-solving rather than basic calculations. Consistent multiplication practice also builds confidence in handling math operations, promoting a positive attitude toward mathematics.
Furthermore, integrating multiplication into daily routines can make learning engaging and relevant. Activities, games, and real-life examples help children see the practical applications of multiplication, sparking curiosity and motivation.
Strong multiplication skills established during early education serve as building blocks for lifelong mathematical competence, benefiting academic performance and everyday numerical tasks. Therefore, prioritizing multiplication practice for young learners sets them up for sustained success and confidence in mathematics.