Problem-Solving Skills Normal Chess Worksheets for Ages 6-7
6 filtered results
-
From - To
Our engaging Problem-Solving Skills Normal Chess Worksheets for ages 6-7 offer young learners a fun and educational way to enhance their critical thinking. These printable worksheets from Kids Academy challenge kids to strategize, observe patterns, and make thoughtful decisions. By introducing key chess concepts, we help children develop cognitive skills and foster a love for problem-solving. Perfect for classroom activities or at-home practice, our chess worksheets transform complex strategies into playful learning experiences, building confidence and laying the foundation for future success. Empower your 6-7-year-old with the logical prowess and mental agility they'll need throughout life.
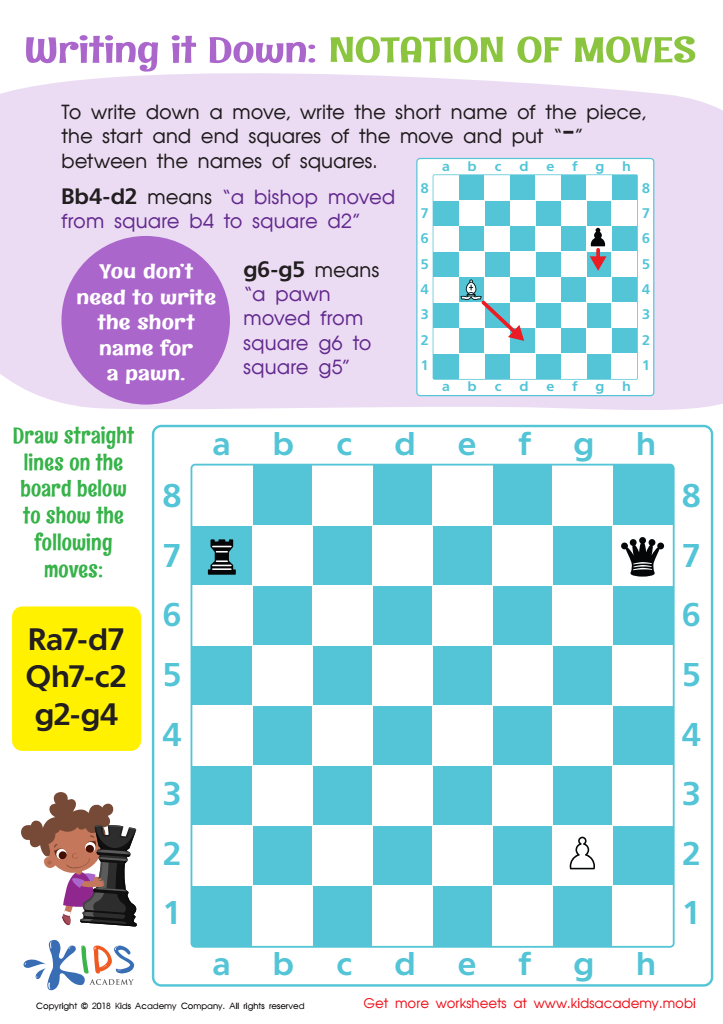

Notation of Moves Writing it Down Worksheet
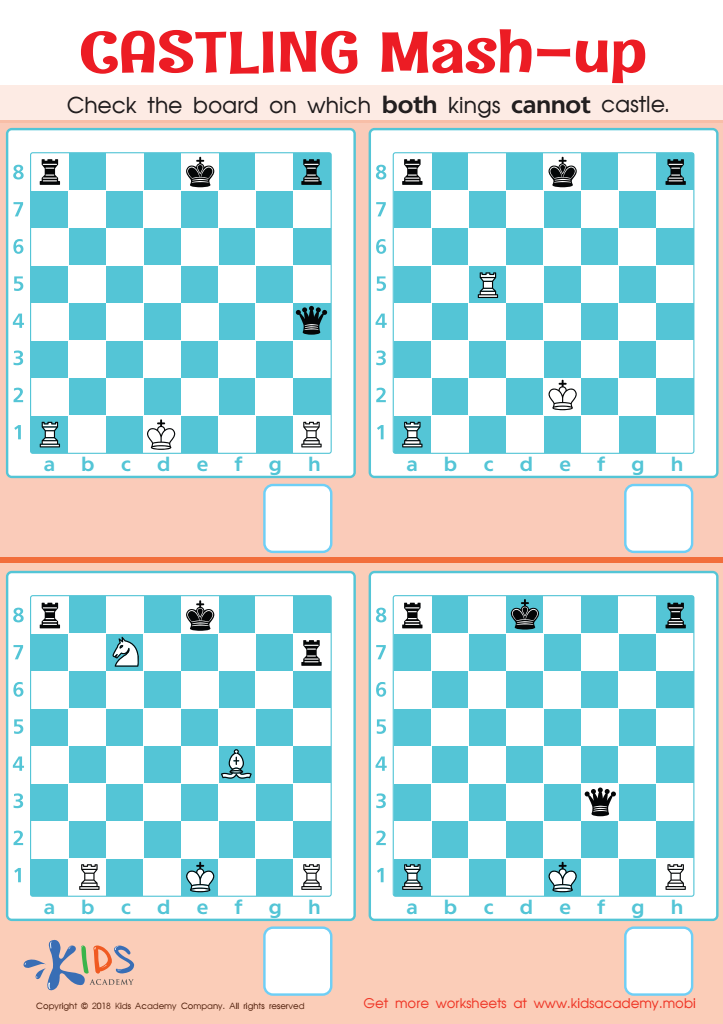

Castling Mash–up Worksheet
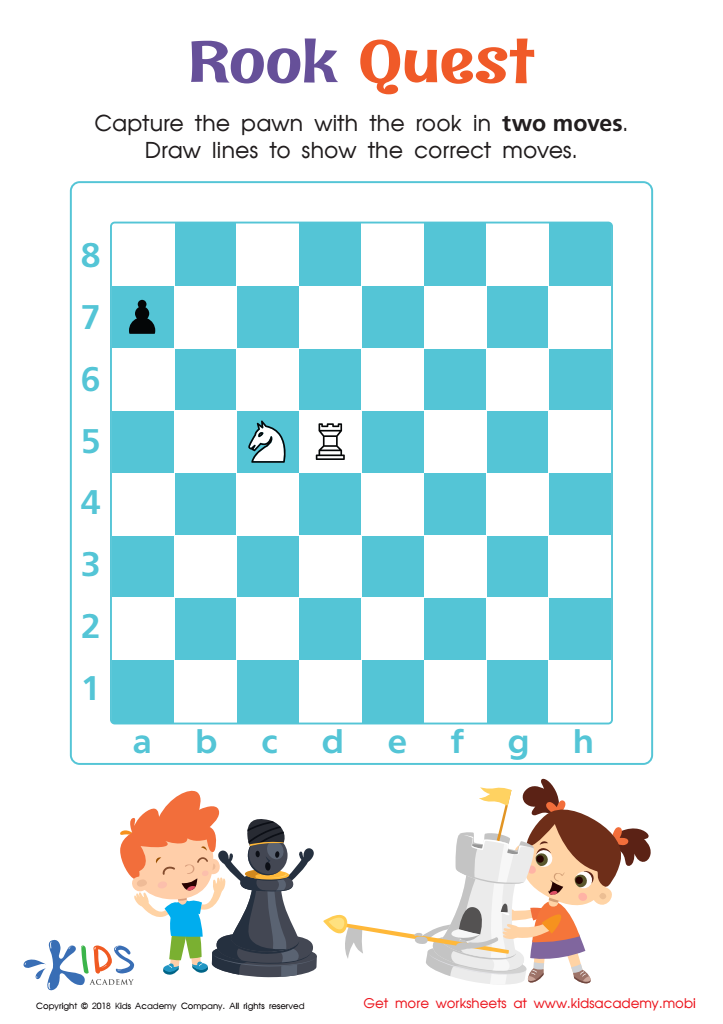

Rook Quest Worksheet
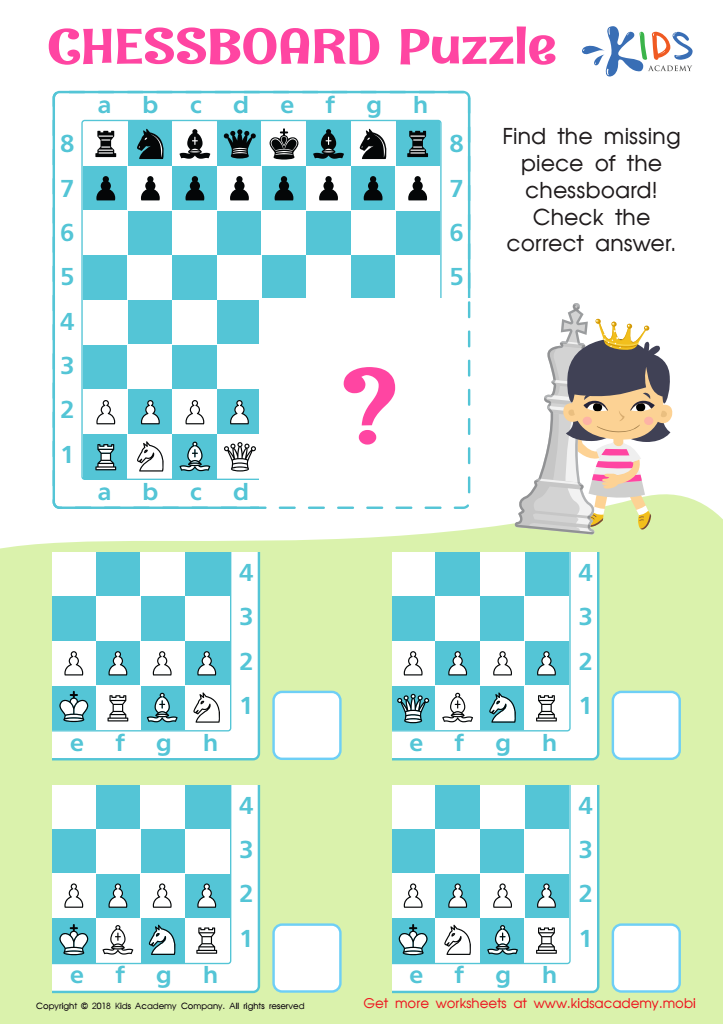

Chessboard Puzzle Worksheet
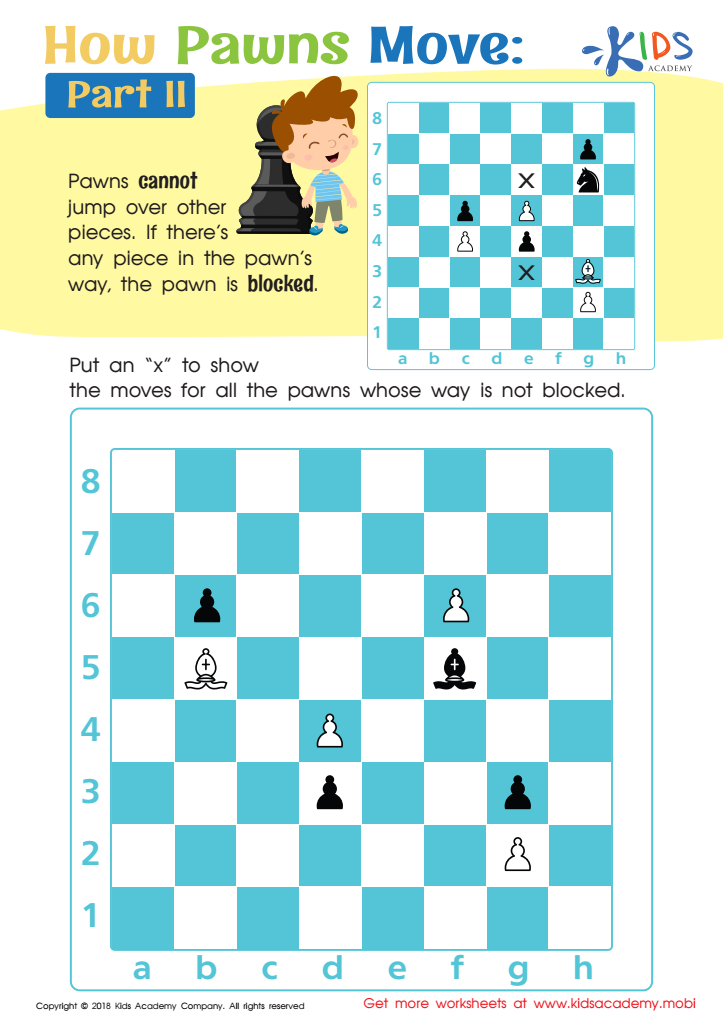

How Pawns Move: Part II Worksheet
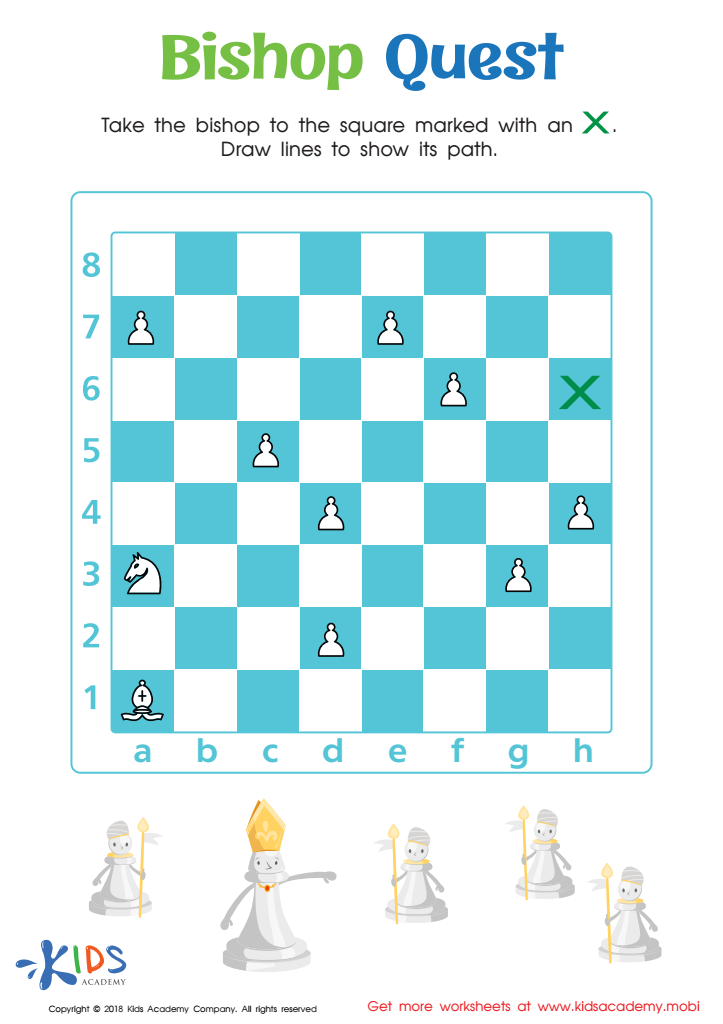

Bishop Quest Worksheet
Parents and teachers should care about developing problem-solving skills in 6-to-7-year-old children through activities like normal chess, as these foundational years are critical for cognitive development. Chess offers a fun and stimulating way to enhance critical thinking, foresight, and decision-making abilities. Each chess move requires players to anticipate possible outcomes and consequences, fostering logical reasoning and planning skills crucial for academic success and life challenges.
Additionally, chess teaches patience and perseverance, as children learn that reaching a solution often requires multiple steps and cannot be rushed. This process can significantly boost their attention span and ability to focus on tasks over extended periods. Chess also nurtures creativity, as players must think outside the box to develop unique strategies against their opponents.
Moreover, the game provides excellent opportunities for social and emotional growth. As children engage with peers in chess, they learn the values of respect, fairness, and sportsmanship. This interactive environment can improve their communication skills and boost their self-esteem.
In summary, integrating chess into the activities for children aged 6-7 can contribute immensely to their overall cognitive, emotional, and social development, equipping them with essential skills that resonate well beyond the chessboard.
 Assign to My Students
Assign to My Students