Step-by-step Guide to A Child's Success in Multiplication
Feb. 23, 2024
Multiplication skills are something that comes in handy on a daily basis -- from totaling grocery costs to calculating room area, or doubling a cake recipe.
Today we'll explore the best ways to teach this important math concept to children. How can we transform this possibly overwhelming task into an exciting journey of exploration for young students?
Whether you're explaining arrays to second graders or exploring various techniques for mastering and applying multiplication facts in third grade, this thorough article covers it all. Plus, we've included some of our multiplication worksheets to enhance the educational experience and make it more enjoyable for both teachers and students!
Introducing Kids to the Concept of Multiplication
Let's begin at the start. Multiplication is essentially a quicker way to add numbers multiple times. If a child knows that 2 + 2 + 2 is 6, then they're progressing towards understanding that 2 times 3 produces the same result.
This foundational knowledge is what makes multiplication less daunting and easier to understand.
Picture having three baskets, each containing four apples. Instead of performing the addition of 4 apples three times to total 12 apples, you can instead calculate the product of 3 (baskets) and 4 (apples per basket) to determine the overall number of apples. That is 3 multiplied by 4, resulting in 12. Simple, isn't it?
Another great benefit from understanding arrays is that they'll provide kids with the foundation for grasping advanced math concepts such as area further on.
Calculating with Help of Groups and Arrays
An effective method for teaching multiplication to a second grader is using visual aids. Students can better understand the concept of multiplication when they have visual and tactile access to the objects being multiplied. This is when groups of objects and arrays can be of great benefit!
Using Groups of Objects as Illustration
Begin with something concrete. Instruct students to organize small items such as counters, blocks, or candy pieces in groups. Request them to form multiple sets with equal quantities and then calculate the overall amount. This interactive exercise not only brings loads of fun but also strengthens the concept of multiplication as adding numbers repeatedly.
Drawing Arrays
After students are confident with physical grouping, proceed to teaching them how to draw arrays.
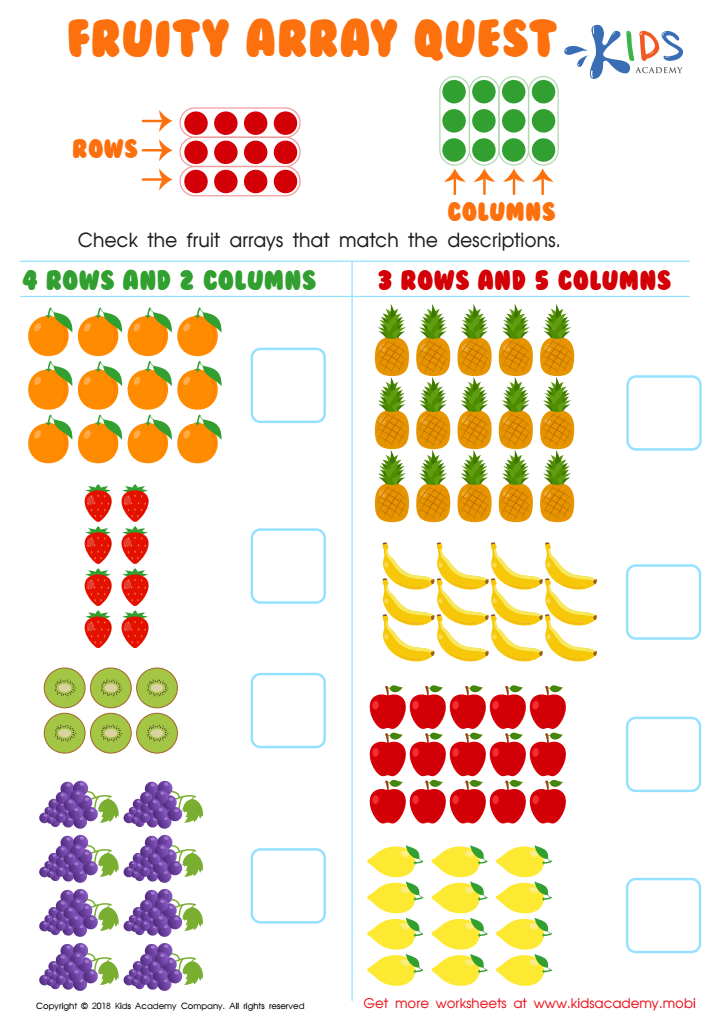
An array is a collection of items organized in a grid format that illustrates a multiplication scenario. Encourage students to create arrays or use one of our arrays resources to help them visualize their multiplication problems. One way to approach this is by having your child tackle this multiplication worksheet called the Fruity Array Quest:
Learning Product Patterns within the Multiplication Table
Patterns can be found in mathematics everywhere, including in the multiplication table. When students begin to recognize these patterns, it's as if a light bulb suddenly turns on. They will observe that when you multiply by 10, the result always ends in zero, and when you multiply by 5, the result ends in either 5 or 0. Identifying these patterns not only aids in memorization but also reveals the predictable elegance of mathematics to curious young minds.
Skip Counting
After students have become familiar with manipulatives, we can move on to abstract thinking by introducing skip counting. Skip counting is just counting based on using any number different than one. It is a critical skill that naturally transitions into multiplication.
- Begin with simple numbers such as 2, 5, or 10, and gradually increase to more complex numbers.
- Utilize rhymes, tunes, or hand-clapping activities to make skip counting fun and unforgettable.
- Encourage students to count out loud together or individually to strengthen the pattern.
Skip counting helps students understand multiplication and improves their number sense, preparing them for the next learning step.
The Commutative Property of Multiplication
Realizing that the product remains the same despite the order of factors is a significant discovery. The commutative property makes learning easier by lessening the amount of information students have to remember. Let's demonstrate for them how it functions.
If you you've learned that 4 multiplied by 3 equals 12, then you also know that 3 multiplied by 4 equals 12. This property helps to acquire two pieces of information simultaneously!
Introduce this property by using pairs of multiplication facts to show the flexibility of multiplication. This straightforward technique can greatly lessen the burden and anxiety for students.
To help your child practice, encourage them to work on multiplication problems like the ones provided in our multiplication worksheets. For example, we suggest that you give this Balance the Scales worksheet a try:
How to Interest Students in Multiplication
Engagement is key in interactive learning. Students are more likely to remember information when they are actively engaged in the learning process. This is particularly evident in multiplication, as the process of learning can easily become monotonous.
By including interactive tasks, you can engage your students are in a dynamic and enjoyable practice of multiplication.
Technology and Games as Handy Tools for Multiplication Mastery
Technology provides numerous opportunities to make learning multiplication an enjoyable experience. There are plenty of digital resources available to aid students in practicing multiplication, ranging from times tables activities to websites with quizzes and worksheets.
Below is another multiplication sheet by Kids Academy that can assist your child in practicing this crucial skill:
Use Collaborative Activities to Encourage Peer Learning
Learning can also be a collaborative experience, rather than just an individual endeavor. Participating in group activities can promote cooperation among students, foster mutual learning, and facilitate the articulation of ideas in their own language. Working with others while learning can enhance comprehension and provide a new viewpoint for students struggling with multiplication.
For example, match students together and have them test each other on multiplication skills. Alternatively, design a group competition in which each team must quickly solve a series of problems. This not only encourages collaboration but also enhances the social and enjoyable aspect of learning multiplication.
As you start this quest of assisting your child in developing multiplication skills, it's important to keep in mind that education is more than just sharing information - it's also about encouraging progress. Multiplication goes beyond being just a math skill; it opens up pathways to problem-solving, critical thinking, and future learning prospects.